| [1] |
ZHU F. Buckwheat proteins and peptides:Biological functions and food applications[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,110:155−167.
|
| [2] |
SOFI S A, AHMED N, FAROOQ A, et al. Nutritional and bioactive characteristics of buckwheat, and its potential for developing gluten-free products:An updated overview[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2023,11(5):2256−2276.
|
| [3] |
NORBÄCK D, WIESLANDER G. A review on epidemiological and clinical studies on buckwheat allergy[J]. Plants-Basel,2021,10(3):607. doi: 10.3390/plants10030607
|
| [4] |
赵霞, 韩一军, 姜利娜, 等. 我国苦荞市场与产业调查分析报告[J]. 农产品市场,2021(15):42−44. [ZHAO Xia, HAN Yijun, JIANG Lina, et al. China's buckwheat market and industry research and analysis report[J]. Agricultural Market,2021(15):42−44.]
ZHAO Xia, HAN Yijun, JIANG Lina, et al. China's buckwheat market and industry research and analysis report[J]. Agricultural Market, 2021(15): 42−44.
|
| [5] |
KIM S A, TOUSHIK S H, LEE J E, et al. Ultrasensitive monoclonal antibodies specific to thermal stable-soluble proteins of buckwheat[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,423:136269. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136269
|
| [6] |
MIYAMOTO M, KATO M, YOSHIHARA S, et al. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome due to buckwheat:A case report[J]. Allergologia et Immunopathologia,2023,51(3):25−27. doi: 10.15586/aei.v51i3.826
|
| [7] |
OLIVIERI B, SKYPALA I J. New arrivals in anaphylaxis to foods[J]. Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology,2023,23(5):357−363. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000936
|
| [8] |
ERQUICI S P, ABRAIRA M B, ARENAS S D, et al. Rhinoconjunctivitis and occupational asthma due to buckwheat flour allergy[J]. Archivos de Bronconeumologia,2020,56(7):466. doi: 10.1016/j.arbr.2020.02.004
|
| [9] |
JUNGEWELTER S, AIRAKSINEN L, PESONEN M. Occupational buckwheat allergy as a cause of allergic rhinitis, asthma, contact urticaria and anaphylaxis-An emerging problem in food-handling occupations?[J]. American Journal of Industrial Medicine,2020,63(11):1047−1053. doi: 10.1002/ajim.23185
|
| [10] |
FAROOQ M, WANI S M, MIR S A, et al. An overview of buckwheat allergy:A rare allergenic food[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2023,123:105616. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2023.105616
|
| [11] |
JUNGEWELTER S, SUOMELA S, AIRAKSINEN L. Occupational IgE-mediated psyllium allergy in contemporary gluten-free and vegan baking:A case of allergic rhinitis[J]. American Journal of Industrial Medicine,2021,64(5):431. doi: 10.1002/ajim.23238
|
| [12] |
SUDHARSON S, KALIC T, HAFNER C, et al. Newly defined allergens in the WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Database during 01/2019-03/2021[J]. Allergy,2021,76(11):3359−3373. doi: 10.1111/all.15021
|
| [13] |
ZHANG Z Y, LI X M, WANG H, et al. Seafood allergy:Allergen, epitope mapping and immunotherapy strategy[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2023,63(10):1314−1338. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2181755
|
| [14] |
LEE A S E, SUPRUN M, SAMPSON H. Epitope-based IgE assays and their role in providing diagnosis and prognosis of food allergy[J]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology-in Practice,2023,11(10):2983−2988. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2023.06.043
|
| [15] |
PLATTS-MILLS T A, HILGER C, JAPPE U, et al. Carbohydrate epitopes currently recognized as targets for IgE antibodies[J]. Allergy,2021,76(8):2383−2394. doi: 10.1111/all.14802
|
| [16] |
MATSUMOTO R, FUJINO K, NAGATA Y, et al. Molecular characterization of a 10-kDa buckwheat molecule reactive to allergic patients' IgE[J]. Allergy,2004,59(5):533−538. doi: 10.1046/j.1398-9995.2003.00412.x
|
| [17] |
张润敏, 刘海宁, 姚慧鹏, 等. 苦荞过敏蛋白TBW17基因克隆及其抗原表位分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2016,35(12):3481−3486. [ZHANG Runmin, LIU Haining, YAO Huipeng, et al. Cloning of buckwheat allergenic protein TBW17 gene and its antigenic epitope analysis[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2016,35(12):3481−3486.]
ZHANG Runmin, LIU Haining, YAO Huipeng, et al. Cloning of buckwheat allergenic protein TBW17 gene and its antigenic epitope analysis[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2016, 35(12): 3481−3486.
|
| [18] |
侯晓军. 苦荞过敏蛋白TB22kDa的cDNA片断克隆、原核表达及初步纯化[D]. 太原:山西大学, 2003. [HOU Xiaojun. Cloning, prokaryotic expression and preliminary purification of cDNA fragment of buckwheat allergenic protein TB22kDa[D]. Taiyuan:Shanxi University, 2003.]
HOU Xiaojun. Cloning, prokaryotic expression and preliminary purification of cDNA fragment of buckwheat allergenic protein TB22kDa[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2003.
|
| [19] |
CUI X D, TIAN W H, WANG W H, et al. Sequence analysis and biochemical characteristics of two non-specific lipid transfer proteins from tartary buckwheat seeds[J]. Protein and Peptide Letters,2023,30(6):520−529. doi: 10.2174/0929866530666230511154511
|
| [20] |
李俊慧, 邵军军, 常惠芸, 等. 抗原表位鉴定方法的研究进展[J]. 中国兽医科学,2021,51(6):678−683. [LI Junhui, SHAO Junjun, CHANG Huiyun, et al. Advances in antigenic epitope identification methods[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science,2021,51(6):678−683.]
LI Junhui, SHAO Junjun, CHANG Huiyun, et al. Advances in antigenic epitope identification methods[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2021, 51(6): 678−683.
|
| [21] |
PARK J Y, CHO S H. Production of monoclonal antibody of heat-labile toxin A subunit to identify enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by epitope mapping using synthetic peptides[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2023,14:1152910. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1152910
|
| [22] |
DANG X B, GUELEN L, HULSIK D L, et al. Epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies:A comprehensive comparison of different technologies[J]. Mabs,2023,15(1):2285285. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2023.2285285
|
| [23] |
JIA B X, OJIMA-KATO T, KOJIMA T, et al. Rapid and cost-effective epitope mapping using pure ribosome display coupled with next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering,2024,137(4):321−328. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2024.01.008
|
| [24] |
JAROSZEWICZ W, MORCINEK-ORLOWSKA J, PIERZYNOWSKA K, et al. Phage display and other peptide display technologies[J]. Fems Microbiology Reviews,2022,46(2):fuab052. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuab052
|
| [25] |
ZHANG A L, ZHAO H J, PEI S H, et al. Identification and structure of epitopes on cashew allergens Ana o 2 and Ana o 3 using phage display[J]. Molecules,2023,28(4):1880. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041880
|
| [26] |
URISU A, KONDO Y, MORITA Y, et al. Isolation and characterization of a major allergen in buckwheat seeds[J]. Current Advances in Buckwheat Research, 1995:965-974.
|
| [27] |
TANAKA K, MATSUMOTO K, AKASAWA A, et al. Pepsin-resistant 16-kD buckwheat protein is associated with immediate hypersensitivity reaction in patients with buckwheat allergy[J]. Journal of Innate Immunity,2002,129(1):49−56.
|
| [28] |
CHOI S Y, SOHN J H, LEE Y W, et al. Characterization of buckwheat 19-kD allergen and its application for diagnosing clinical reactivity[J]. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology,2007,144(4):267−274. doi: 10.1159/000106315
|
| [29] |
FUJIMURA M, MINAMI Y, WATANABE K, et al. Purification, characterization, and sequencing of a novel type of antimicrobial peptides, Fa-AMP1 and Fa-AMP2, from seeds of buckwheat ( Fagopyrum esculentum Moench.)[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry,2003,67(8):1636−1642. doi: 10.1271/bbb.67.1636
|
| [30] |
GEISELHART S, NAGL C, DUBIELA P, et al. Concomitant sensitization to legumin, Fag e 2 and Fag e 5 predicts buckwheat allergy[J]. Clinical & Experimental Allergy,2018,48(2):217−224.
|
| [31] |
HU F, YE Z Y, DONG K, et al. Divergent structures and functions of the cupin proteins in plants[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,242:124791. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124791
|
| [32] |
SANO M, NAKAGAWA M, OISHI A, et al. Diversification of 13S globulins, allergenic seed storage proteins, of common buckwheat[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,155:192−198. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.01.047
|
| [33] |
ZHOU Y, OUYANG B, DU L, et al. Effects of ultra-high-pressure treatment on the structural and functional properties of buckwheat 13S globulin[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2022,11(4):895−903. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.03.008
|
| [34] |
CHNAPEK M, GÁLOVÁ Z, BALÁZOVÁ Z, et al. Application of two-dimensional electrophoresis and mass spectrometry for the detection of allergens in selected varieties of wheat, oats and buckwheat[J]. Journal of Microbiology Biotechnology and Food Sciences,2023,13(1):e9934. doi: 10.55251/jmbfs.9934
|
| [35] |
MARUYAMA FUNSTSUKI W, FUJINO K, SUZUKI T, et al. Quantification of a major allergenic protein in common buckwheat cultivars by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)[J]. Fagopyrum,2004,21:39−44.
|
| [36] |
YOSHIOKA H, OHMOTO T, URISU A, et al. Expression and epitope analysis of the major allergenic protein Fag e 1 from buckwheat[J]. 2004, 161(7):761-767.
|
| [37] |
YANAGIDA N, SATO S, MARUYAMA N, et al. Specific IgE for Fag e 3 predicts oral buckwheat food challenge test results and anaphylaxis:A pilot study[J]. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology,2018,176(1):8−14. doi: 10.1159/000487135
|
| [38] |
SOUZA P F. The forgotten 2S albumin proteins:Importance, structure, and biotechnological application in agriculture and human health[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,164:4638−4649. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.049
|
| [39] |
BUENO D C, MARTÍN P L, PARRÓN J, et al. Characterization of relevant biomarkers for the diagnosis of food allergies:An overview of the 2S albumin family[J]. Foods,2021,10(6):1235. doi: 10.3390/foods10061235
|
| [40] |
CHOI S Y, SOHN J H, LEE Y W, et al. Application of the 16-kDa buckwheat 2 S storage albumin protein for diagnosis of clinical reactivity[J]. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, 2007, 99(3):254−260.
|
| [41] |
SATOH R, KOYANO S, TAKAGI K, et al. Identification of an IgE-binding epitope of a major buckwheat allergen, BWp16, by SPOTs assay and mimotope screening[J]. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology,2010,153(2):133−140. doi: 10.1159/000312630
|
| [42] |
DI SOMMA A, MORETTA A, CANÈ C, et al. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm peptides[J]. Biomolecules,2020,10(4):652. doi: 10.3390/biom10040652
|
| [43] |
SATHOFF A E, LEWENZA S, SAMAC D A. Plant defensin antibacterial mode of action against Pseudomonas species[J]. Bmc Microbiology,2020,20(1):1−11. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1672-7
|
| [44] |
BROEKAERT W F, CAMMUE B P, DE BOLLE M F, et al. Antimicrobial peptides from plants[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences,1997,16(3):297−323. doi: 10.1080/07352689709701952
|
| [45] |
GEISELHART S, NAGL C, DUBIELA P, et al. Concomitant sensitization to legumin, Fag e 2 and Fag e 5 predicts buckwheat allergy[J]. 2018, 48(2):217−224.
|
| [46] |
LUTHAR Z, GOLOB A, GERM M, et al. Tartary buckwheat in human nutrition[J]. Plants-Basel,2021,10(4):700. doi: 10.3390/plants10040700
|
| [47] |
KOYANO S, TAKAGI K, TESHIMA R, et al. Molecular cloning of cDNA, recombinant protein expression and characterization of a buckwheat 16-kDa major allergen[J]. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology,2006,140(1):73−81. doi: 10.1159/000092038
|
| [48] |
ZHANG X, YUAN J M, CUI X D, et al. Molecular cloning, recombinant expression, and immunological characterization of a novel allergen from tartary buckwheat[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2008,56(22):10947−10953. doi: 10.1021/jf801855a
|
| [49] |
CHEN F, LI H, FAN X, et al. Identification of a novel major allergen in buckwheat seeds:Fag t 6[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(45):13315−13322. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01537
|
| [50] |
郑蓓. 苦荞16 kDa过敏原Fag t 2结构与功能研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2021. [ZHEN Pei. Structure and function of the buckwheat 16 kDa allergen, Fag t 2[D]. Yangling:North West Agriculture and Forestry University, 2021.]
ZHEN Pei. Structure and function of the buckwheat 16 kDa allergen, Fag t 2[D]. Yangling: North West Agriculture and Forestry University, 2021.
|
| [51] |
CHEN P, GUO Y, YAN Q, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of Fag t 2:A 16‐kDa major allergen from Tartary buckwheat seeds[J]. Allergy,2011,66(10):1393−1395. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02657.x
|
| [52] |
ZHENG B, ZHANG H, SHEN W, et al. Core epitope analysis of 16 kDa allergen from tartary buckwheat[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,346:128953. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128953
|
| [53] |
贺东亮, 张政, 任晓霞, 等. 苦荞过敏原TBa和TBb基因的共表达及其包涵体复性的研究[J]. 中国农学通报,2009,25(8):50−52. [HE Dongliang, ZHANG Zheng, REN Xiaoxia, et al. Co-expression of TBa and TBb genes of buckwheat allergens and their inclusion body complexes[J]. China Agronomy Bulletin,2009,25(8):50−52.]
HE Dongliang, ZHANG Zheng, REN Xiaoxia, et al. Co-expression of TBa and TBb genes of buckwheat allergens and their inclusion body complexes[J]. China Agronomy Bulletin, 2009, 25(8): 50−52.
|
| [54] |
YANG Z, LI Y, LI C, et al. Synthesis of hypoallergenic derivatives of the major allergen Fag t 1 from tartary buckwheat via sequence restructuring[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2012,50(8):2675−2680. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2012.03.039
|
| [55] |
REN X, ZHANG X, LI Y, et al. Epitope mapping and immunological characterization of a major allergen TBa in tartary buckwheat[J]. Biotechnology Letters,2010,32:1317−1324. doi: 10.1007/s10529-010-0281-1
|
| [56] |
赵小珍, 张政, 景巍, 等. 苦荞麦主要过敏蛋白N端基因片段的克隆及序列分析[J]. 食品科学,2006(10):41−44. [ZHAO Xiaozhen, ZHANG Zheng, JING Wei, et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of the N-terminal gene fragment of buckwheat major allergenic protein[J]. Food Science,2006(10):41−44.]
ZHAO Xiaozhen, ZHANG Zheng, JING Wei, et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of the N-terminal gene fragment of buckwheat major allergenic protein[J]. Food Science, 2006(10): 41−44.
|
| [57] |
贺东亮, 崔晓东, 赵小珍, 等. 过敏蛋白TBb的免疫活性鉴定及其表位预测[J]. 免疫学杂志,2009,25(2):137−140,144. [HE Dongliang, CUI Xiaodong, ZHAO Xiaozhen, et al. Identification of immunoreactivity of the allergenic protein TBb and its epitope prediction[J]. Journal of Immunology,2009,25(2):137−140,144.]
HE Dongliang, CUI Xiaodong, ZHAO Xiaozhen, et al. Identification of immunoreactivity of the allergenic protein TBb and its epitope prediction[J]. Journal of Immunology, 2009, 25(2): 137−140,144.
|
| [58] |
LI P, CUI X, LI Y, et al. Epitope mapping and identification on a 3D model built for the tartary buckwheat allergic protein TBb[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin,2011,43(6):441−447. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmr036
|
| [59] |
BOARD A J, CROWTHER J M, ACEVEDO-FANI A, et al. How plants solubilise seed fats:Revisiting oleosin structure and function to inform commercial applications[J]. Biophysical Reviews,2022,14(1):257−266. doi: 10.1007/s12551-021-00923-5
|
| [60] |
HE X R, YANG Y, CHEN Y X, et al. Immunoglobulin e epitope mapping and structure-allergenicity relationship analysis of crab allergen scy p 9[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2023,71(45):17379−17390.
|
| [61] |
TAHIR S, BOURQUARD T, MUSNIER A, et al. Accurate determination of epitope for antibodies with unknown 3D structures[J]. Mabs,2021,13(1):1961349. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.1961349
|
| [62] |
MARINI-RAPOPORT O, FERNÁNDEZ-QUINTERO M L, KESWANI T, et al. Defining the cross-reactivity between peanut allergens Ara h 2 and Ara h 6 using monoclonal antibodies[J]. Clinical and Experimental Immunology,2024,216(1):25−35. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxae005
|
| [63] |
POM A, SMITH S A, CHRUSZCZ M, et al. Precision engineering for localization, validation, and modification of allergenic epitopes[J]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology,2024,153(3):560−571. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.12.017
|






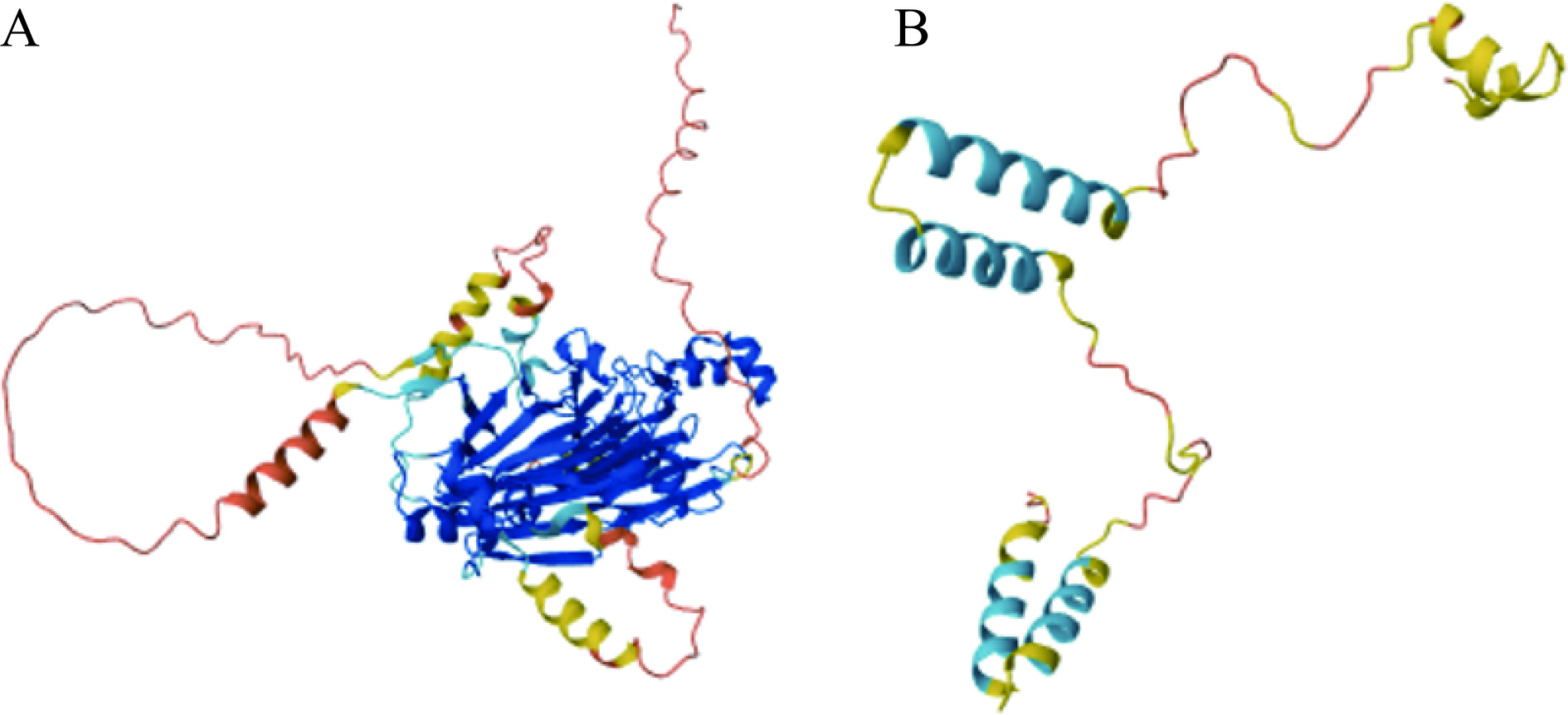

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: