| [1] |
|
| [2] |
SAKAČ M, TORBICA A, SEDEJ I, et al. Influence of breadmaking on antioxidant capacity of gluten free breads based on rice and buckwheat flours[J]. Food Research International,2011,44(9):2806−2813. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.06.026
|
| [3] |
DING Y, YANG L, XIA Y, et al. Effects of frying on starch structure and digestibility of glutinous rice cakes[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2018,83:196−203. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2018.08.014
|
| [4] |
WU Y, CHEN Z, LI X, et al. Effect of tea polyphenols on the retrogradation of rice starch[J]. Food Research International,2009,42(2):221−225. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2008.11.001
|
| [5] |
LIU H, GUO X, LI W, et al. Changes in physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of common buckwheat starch by heat-moisture treatment and annealing[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,132:237−244. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.071
|
| [6] |
HU J, LI X, CHENG Z, et al. Modified Tartary buckwheat ( Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn.) starch by gaseous ozone: Structural, physicochemical and in vitro digestible properties[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,125:107365. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107365
|
| [7] |
ZHANG Z, TIAN J, FANG H, et al. Physicochemical and digestion properties of potato starch were modified by complexing with grape seed proanthocyanidins[J]. Molecules,2020,25(5):1123. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051123
|
| [8] |
ALVAREZ-POBLANO L, ROMAN-GUERRERO A, VERNON-CARTER E, et al. Exogenous addition of muicle ( Justicia spicigera Schechtendal) extract to white maize tortillas affects the antioxidant activity, texture, color, and in vitro starch digestibility[J]. LWT,2020,133:110120. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110120
|
| [9] |
谭沙, 朱仁威, 刘庆庆, 等. 外源添加物对淀粉理化性质和消化特性影响的研究进展[J/OL]. 中国粮油学报: 1−9 [2022-06-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2864.TS.20220325.1023.012.html
TAN S, ZHU R W, LIU Q Q, et al. Research progress on the effects of exogenous additives on the physicochemical properties and digestibility of starch[J/OL]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association: 1−9 [2022-06-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2864.TS.20220325.1023.012.html
|
| [10] |
王明福, 滕静. 多酚类化合物在食品热加工中的化学与生物活性变化及其对食品品质的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2017,17(6):1−12. [WANG M F, TENG J. Changes in chemical and biological activities of polyphenolic compounds in food thermal processing and their effects on food quality[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2017,17(6):1−12. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2017.06.001
|
| [11] |
SĘCZYK Ł, SUGIER D, ŚWIECA M, et al. The effect of in vitro digestion, food matrix, and hydrothermal treatment on the potential bioaccessibility of selected phenolic compounds[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,344:128581. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128581
|
| [12] |
WANG L, WANG L, WANG T, et al. Comparison of quercetin and rutin inhibitory influence on Tartary buckwheat starch digestion in vitro and their differences in binding sites with the digestive enzyme[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,367:130762. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130762
|
| [13] |
DU J, YAO F, ZHANG M, et al. Effect of persimmon tannin on the physicochemical properties of maize starch with different amylose/amylopectin ratios[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,132:1193−1199. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.046
|
| [14] |
PAN J, LI M, ZHANG S, et al. Effect of epigallocatechin gallate on the gelatinisation and retrogradation of wheat starch[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,294:209−215. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.05.048
|
| [15] |
ZHU S, LIU B, WANG F, et al. Characterization and in vitro digestion properties of cassava starch and epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) blend[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020:110398.
|
| [16] |
WU Y, NIU M, XU H. Pasting behaviors, gel rheological properties, and freeze-thaw stability of rice flour and starch modified by green tea polyphenols[J]. LWT,2020,118:108796. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108796
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
GAO L, WANG H, WAN C, et al. Structural, pasting and thermal properties of common buckwheat ( Fagopyrum esculentum Moench ) starches affected by molecular structure[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,156:120−126. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.064
|
| [19] |
彭登峰, 柴春祥, 张坤生, 等. 超高压处理对荞面碗托品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报,2014,26(4):1055−1061. [PENG D F, CHAI C X, ZHANG K S, et al. Effect of ultra-high pressure treatment on quality of buckwheat wantuo[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2014,26(4):1055−1061.
|
| [20] |
SUN X, YU C, FU M, et al. Extruded whole buckwheat noodles: Effects of processing variables on the degree of starch gelatinization, changes of nutritional components, cooking characteristics and in vitro starch digestibility[J]. Food & Function,2019,10(10):6362−6373.
|
| [21] |
BAKAR M F A, MOHAMED M, RAHMAT A, et al. Phytochemicals and antioxidant activity of different parts of bambangan ( Mangifera pajang) and tarap ( Artocarpus odoratissimus)[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,113(2):479−483. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.07.081
|
| [22] |
RE R, PELLEGRINI N, PROTEGGENTE A, et al. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay[J]. Free radical Biology and Medicine,1999,26(9−10):1231−1237. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3
|
| [23] |
BENZIE I F, STRAIN J J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,1996,239(1):70−76. doi: 10.1006/abio.1996.0292
|
| [24] |
GOH R, GAO J, ANANINGSIH V K, et al. Green tea catechins reduced the glycaemic potential of bread: An in vitro digestibility study[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,180:203−210. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.02.054
|
| [25] |
GOÑI I, GARCIA-ALONSO A, SAURA-CALIXTO F. A starch hydrolysis procedure to estimate glycemic index[J]. Nutrition Research, 1997, 17: 427−437.
|
| [26] |
彭登峰, 柴春祥, 张坤生, 等. 不同解冻方式对冷冻荞面碗托品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报,2014,26(3):592−597. [PENG D F, CAI C X, ZHANG K S, et al. Effects of different thawing methods on quality of buckwheat wantuo[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2014,26(3):592−597. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2014.03.10
|
| [27] |
NA L, TAYLOR L S, FERRUZZI M G, et al. Color and chemical stability of tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in solution and solid states[J]. Food Research International,2013,53(2):909−921. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.11.019
|
| [28] |
FAN W, CHEN Y, SUN J, et al. Effects of tea polyphenol on quality and shelf life of pork sausages[J]. Journal of Food science and Technology,2014,51(1):191−195. doi: 10.1007/s13197-013-1076-x
|
| [29] |
LI C, DHITAL S, GILBERT R G, et al. High-amylose wheat starch: Structural basis for water absorption and pasting properties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,245:116557. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116557
|
| [30] |
谢亚敏, 许飞, 陈洁, 等. 多酚与淀粉相互作用对板栗淀粉特性的影响[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2021,42(5):30−38. [XIE Y M, XU F, CHEN J, et al. Study on the interaction between polyphenols and starch and its effect on chesnut starch properties[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,42(5):30−38. doi: 10.16433/j.1673-2383.2021.05.004
|
| [31] |
HAN X, ZHANG M, ZHANG R, et al. Physicochemical interactions between rice starch and different polyphenols and structural characterization of their complexes[J]. LWT,2020,125:109227. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109227
|
| [32] |
SEVENOU O, HILL S, FARHAT I, et al. Organisation of the external region of the starch granule as determined by infrared spectroscopy[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2002,31(1-3):79−85. doi: 10.1016/S0141-8130(02)00067-3
|
| [33] |
ZHU F. Interactions between starch and phenolic compound[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2015,43(2):129−143.
|
| [34] |
张连水, 聂志矗, 赵晓辉, 等. 表儿茶素类单质红外光谱特性研究[J]. 茶叶,2009,35(3):152−156. [ZHANG L S, NIE Z C, ZHAO X H. Study on epicatechins by infrared spectroscope[J]. Journal of Tea,2009,35(3):152−156.
|
| [35] |
BOHN T. Dietary factors affecting polyphenol bioavailability[J]. Nutrition Reviews,2014,72(7):429−452. doi: 10.1111/nure.12114
|
| [36] |
GUO P, YU J, COPELAND L, et al. Mechanisms of starch gelatinization during heating of wheat flour and its effect on in vitro starch digestibility[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,82:370−378. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.04.012
|
| [37] |
GARCIA-VALLE D E, BELLO-PÉREZ L A, AGAMA-ACEVEDO E, et al. Effects of mixing, sheeting, and cooking on the starch, protein, and water structures of durum wheat semolina and chickpea flour pasta[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,360:129993. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129993
|
| [38] |
VAN SOEST J J G, TOURNOIS H, DE WIT D, et al. Short-range structure in (partially) crystalline potato starch determined with attenuated total reflectance FTIR[J]. Carbohydrate Research,1995,279:201−214. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(95)00270-7
|
| [39] |
YAN Z, ZHONG Y, DUAN Y, et al. Antioxidant mechanism of tea polyphenols and its impact on health benefits[J]. Animal Nutrition,2020,6(2):115−123. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.01.001
|
| [40] |
缪铭, 张涛, 沐万孟, 等. 淀粉的支链精细结构与消化性能[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(9):12−15. [MIAO M, ZHANG T, MU W M, et al. Relationship between fine structure of amylopectin and digestibility from cereal starch[J]. Chinese Food Science,2010,31(9):12−15.
|
| [41] |
LI C, GONG B, HU Y, et al. Combined crystalline, lamellar and granular structural insights into in vitro digestion rate of native starches[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,105:105823. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105823
|
| [42] |
ZHU J, ZHANG B, TAN C P, et al. Effect of rosa Roxburghii juice on starch digestibility: A focus on the binding of polyphenols to amylose and porcine pancreatic α-amylase by molecular modeling[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,123:106966. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106966
|
| [43] |
QIN R, YU J, LI Y, et al. Structural changes of starch-lipid complexes during postprocessing and their effect on in vitro enzymatic digestibility[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67:1530−1536. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06371
|
| [44] |
CHI C, LI X, ZHANG Y, et al. Modulating the in vitro digestibility and predicted glycemic index of rice starch gels by complexation with gallic acid[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,89:821−828. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.11.016
|
| [45] |
JIANG C, CHEN Y, YE X, et al. Three flavanols delay starch digestion by inhibiting α-amylase and binding with starch[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,172:503−514. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.070
|
| [46] |
MYA B, BO L, FANG Z, et al. Interactions between caffeic acid and corn starch with varying amylose content and their effects on starch digestion[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,114:106544. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106544
|
| [47] |
ZHU S, LIU B, WANG F, et al. Characterization and in vitro digestion properties of cassava starch and epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) blend[J]. LWT,2021,137:110398. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110398
|
| [48] |
刘盼盼, 邓余良, 尹军峰, 等. 绿茶滋味量化及其与化学组分的相关性研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2014(12):173−181. [LIU P P, DENG Y L, YIN J F, et al. Quantification of green tea taste and its correlation with chemical components[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2014(12):173−181. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2014.12.029
|






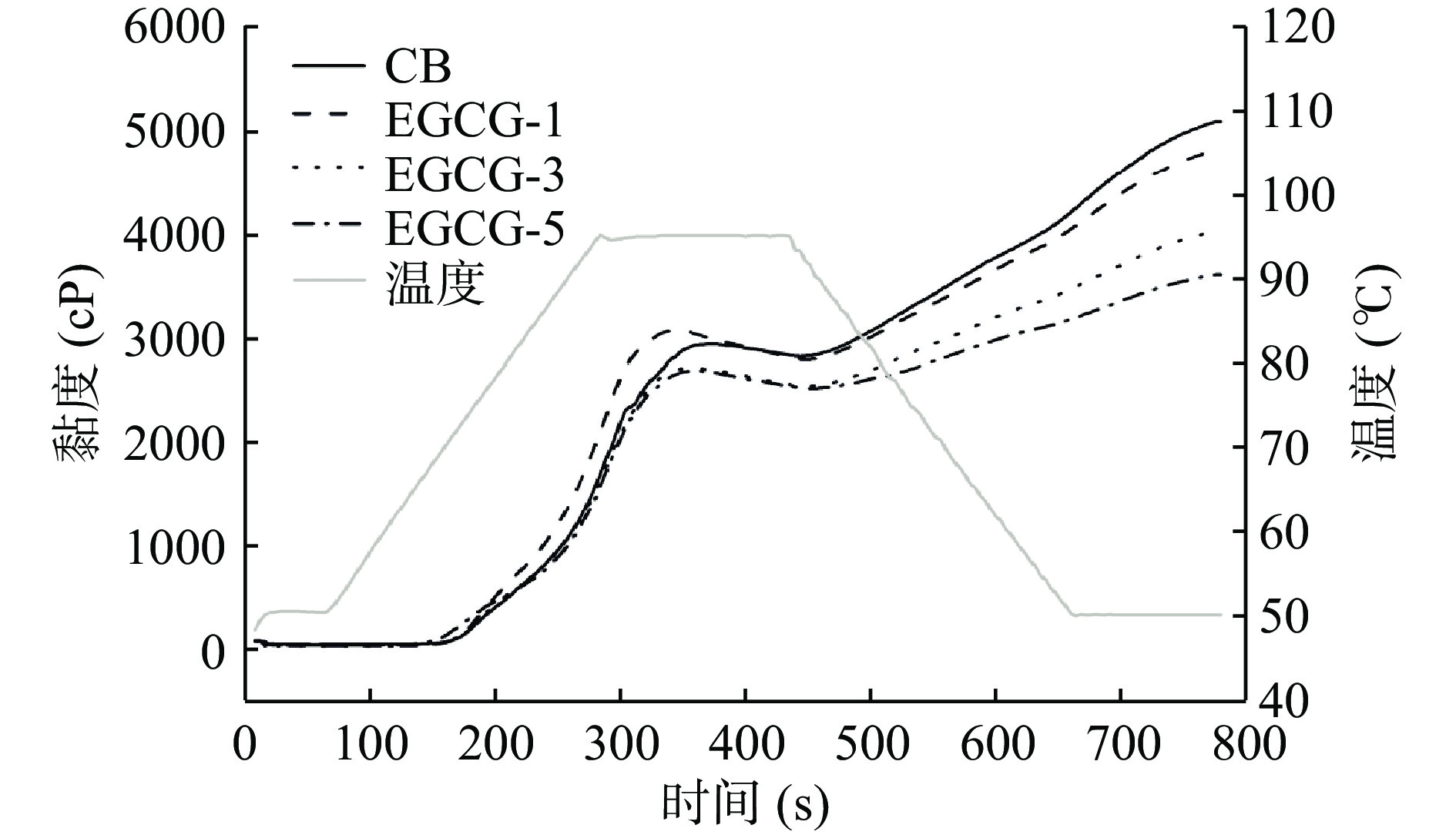

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: