Optimization of Extraction Process and Evaluation of Antioxidant and Antitumor Activities of Total Flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata
-
摘要: 本实验旨在优化半枝莲总黄酮提取工艺,评价半枝莲总黄酮纯化物抗氧化、抗肿瘤活性。采用单因素实验结合响应面Box-Behnken设计对半枝莲总黄酮提取工艺进行研究,主要考察了提取时间、料液比、提取温度和乙醇体积分数对黄酮得率的影响,从而得出半枝莲总黄酮提取的最佳工艺;采用DPPH、ABTS法检测半枝莲总黄酮纯化物的抗氧化活性;采用MTT法检测纯化物对NCI-H1299、HepG2、MHCC-97H、HuH-7细胞增殖的影响。结果表明,半枝莲总黄酮提取最佳工艺为提取时间93 min、料液比1:41(g/mL)、提取温度为68 ℃、乙醇体积分数为75%,该条件下半枝莲总黄酮得率为26.46 mg/g。抗氧化实验结果表明,半枝莲总黄酮纯化物对DPPH、ABTS+自由基有较好的清除作用,IC50值分别为25.41、70.41 μg/mL;抗肿瘤实验表明,在一定浓度范围内不同质量浓度的半枝莲总黄酮纯化物对肿瘤细胞增殖均有一定抑制作用,其NCI-H1299、HepG2、MHCC-97H、HuH-7细胞的IC50值分别为168.6、330.5、269.2、335.8 μg/mL。综上可知,该方法稳定可行、重复性好,能有效提取出半枝莲中总黄酮成分,且纯化后的半枝莲总黄酮具有良好的抗氧化及抗肿瘤活性,可以进行功能性食品的研发。Abstract: The purpose of this experiment was to optimize the extraction process of total flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata and to evaluate the antioxidant and antitumor activity of total flavonoids. A single factor experiment combined with a response surface Box-Behnken design was used to study the extraction process of total flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata. The effects of extraction time, material-to-liquid ratio, extraction temperature and volume fraction of ethanol on the yield of flavonoids were investigated to arrive at the optimal extraction process of total flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata. The antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata was detected by DPPH and ABTS methods, and the effect of purified products on the proliferation of NCI-H1299, HepG2, MHCC-97H and HuH-7 cells were analyzed using the MTT assay. The results showed that the optimum extraction conditions of total flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata were as follows: Extraction time 93 min, ratio of material to liquid 1:41 (g/mL), extraction temperature 68 ℃, volume fraction of ethanol 75%. Under these conditions, the yield of total flavonoids was 26.46 mg/g. The results of antioxidant experiments showed that the purified total flavonoids of Scutellaria barbata had good scavenging effects on DPPH and ABTS+ radicals, with IC50 values of 25.41 and 70.41 μg/mL, respectively. The results of anti-tumor experiments showed that the purified total flavonoids of Scutellaria barbata at different mass concentrations within a certain concentration range had certain inhibitory effects on the proliferation of tumor cells, with the IC50 values of NCI-H1299, HepG2, MHCC-97H and HuH-7 cells were 168.6, 330.5, 269.2 and 335.8 μg/mL, respectively. In summary, it could be concluded that the method was stable and feasible, reproducible, and could effectively extract the total flavonoid components from Scutellaria barbata, and the purified Scutellaria barbata total flavonoids had good antioxidant and antitumor activities, which could be used for the development of functional foods or pharmaceuticals.
-
半枝莲为唇形科黄芩属植物半枝莲(Scutellaria barbata D.Don)的干燥全草,又名通经草、野夏枯草、并头草等[1]。在世界范围内分布广泛,喜湿,常生于田边或湿润草地上[2]。虽尚未正式纳入药食同源及保健食品可用名录,但被广泛开发用于药品、保健品、动物喂养饲料等行业。半枝莲作为公认的抗癌中药[3],味辛、苦,具有清热解毒、祛瘀止血、利水消肿的作用[4]。目前,从半枝莲中已分离出萜类[5]、黄酮类[6]、生物碱类、多糖和挥发油等多种活性成分[7],此外,还富含人体必需的氨基酸、维生素及微量元素[8]。因其显著的药理价值和营养价值可广泛地用于医药、食品、日用化工等多领域的开发。
半枝莲中的黄酮类化合物为主要的活性物质,具有强化免疫系统[9]、抗自由基氧化、调节内分泌功能[10]、影响血管的脆性与渗透性[11]、改善血液循环等[12]诸多生理功能。同时,现已证实黄酮类成分是人体必需的营养成分,可对人体起重要的保健作用[13]。但人体自身不能合成,只能通过外界摄取[14],故此对黄酮类成分用于食品及保健品的研究与开发也将具有更高的经济效益与社会效益。
目前对于黄酮的提取方法主要有热水提取法[15]、超声波提取法[16]、微波提取法[17]、半仿生-酶法提取[18]等。有研究表明这些方法或多或少存在操作较为复杂,提取杂质多,不适用工业化生产等缺陷,相比较而言溶剂提取法试剂用量少、提取时间短、提取较为完全、杂质少[19]。同时,采用乙醇作为溶剂,可降低生产成本及减少对环境造成的污染。黄酮的测定方法主要有紫外分光光度法、高效液相色谱法、液质联用技术等[20−21]。其中紫外分光光度法可快速测定黄酮成分,操作简便。目前,对于半枝莲总黄酮的研究主要集中在黄酮的提取与抗氧化层面,对提取纯化后的总黄酮在抗氧化、抗肿瘤的研究成果较少,结合现代科学技术对半枝莲总黄酮提取方式及药理作用的相关研究是药材资源合理利用及相关疾病药物的开发应用的重要前提。因此,本文选用半枝莲为研究对象,采用溶剂提取法探讨半枝莲总黄酮的提取工艺,考察了提取时间、料液比、提取温度、乙醇体积分数对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响;采用响应面Box-Behnken设计优化半枝莲总黄酮提取工艺,并初步评价半枝莲总黄酮提取物的抗氧化及抗肿瘤活性。以期提高半枝莲黄酮类化合物的提取效率及对半枝莲资源的深入开发具有一定的借鉴意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
半枝莲 购自湖南中医药大学第一附属医院,经该院张裕民主任药师鉴定为唇形科植物半枝莲Scutellaria barbata D.Don的干燥全草;芦丁对照品(纯度≥98%)、维生素C对照品(纯度≥99%) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;AB-8大孔吸附树脂 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、2, 2'-联氮-双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二胺盐(ABTS) 阿拉丁试剂(上海)有限公司;DMEM培养基、胎牛血清、青链双抗、PBS、0.25%胰酶消化液、人肝癌HepG2细胞(CL-0103) 武汉普诺赛生命科技有限公司;噻唑蓝溴化四唑MTT 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;二甲基亚砜DMSO 美国Sigma公司;其他有机试剂均为分析纯 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;人高转移性肝癌MHCC-97H细胞(IM-H045)、人肝癌HuH-7细胞(CL-0120)、人非小细胞肺癌NCI-H1299细胞(CRL-5803) 均由湖南中医药大学药学院教研室馈赠。
DK-98-ⅡA恒温水浴锅 天津市泰斯特仪器有限公司;DHG-9123A电热鼓风干燥箱、BPN-150CRHCO2培养箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;AX223ZH电子分析天平 奥豪斯公司;UV-9000S紫外可见分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;Enspire多功能酶标仪 Perkinelmer公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 半枝莲总黄酮含量测定及得率计算
1.2.1.1 芦丁标准曲线的制备
精密称定芦丁对照品20 mg,80%乙醇溶解,制成浓度为0.2 mg/mL的标准储备液,备用。
1.2.1.2 检测波长的选择
参考文献[22−23]的方法,并稍作修改,吸取芦丁储备液1.0 mL于10 mL的容量瓶中,加入5%亚硝酸钠溶液0.4 mL摇匀,静置6 min;后加10%硝酸铝溶液0.4 mL摇匀,静置6 min;再加4%氢氧化钠溶液4 mL,80%乙醇定容,摇匀,静置15 min。以80%乙醇作为参比溶液,在100~900 nm进行波长扫描,发现在506 nm处有最大吸收波长,故选择其作为检测波长。
1.2.1.3 标准曲线的绘制
精密吸取上述储备液0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0、3.5、4.0 mL于10 mL容量瓶中(不足4.0 mL的加80%乙醇至4.0 mL),采用1.2.1.2方法下的操作测定吸光度,绘制以芦丁质量浓度为横坐标(X),吸光度为纵坐标(A)的标准曲线,得方程为A=15.738x−0.0628,R2=0.9994,在0.01~0.08 mg/mL下线性范围良好。
1.2.1.4 样品测定
将半枝莲药材粉碎,过4号筛后避光保存,备用。准确称取半枝莲粉末5.0 g,置250 mL具塞锥形瓶中,加入75%的乙醇150 mL,在温度为75 ℃下回流提取90 min,提取2次,放冷后用五层纱布过滤,合并两次滤液,60 ℃减压浓缩后转移至25 mL容量瓶中定容,得样品溶液。精密吸取样品溶液1 mL于10 mL容量瓶中定容,得样品待测溶液。精密吸取样品待测溶液1 mL于10 mL容量瓶中,按照1.2.1.2方法下显色方法于506 nm处测定吸光度(A),代入回归方程中计算总黄酮的质量浓度(C),计算半枝莲总黄酮得率(Y)的公式如下[24]:
Y=C×D×VM 式中:Y为半枝莲总黄酮得率,mg/g;C为提取液中总黄酮质量浓度,mg/mL;D为稀释倍数;V为样品溶液总体积,mL;M为半枝莲的质量,g。
1.2.2 单因素实验
精密称取半枝莲粉末,每份5.0 g,在设定的实验条件下回流提取2次,过滤,合并滤液,减压浓缩至25 mL容量瓶中,得半枝莲总黄酮提取液。每组实验平行3次,按照1.2.1.2方法下测定吸光度,并根据公式计算半枝莲总黄酮得率。
1.2.2.1 不同提取时间对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响
设定料液比1:30 g/mL,提取温度75 ℃,乙醇体积分数75%,考察提取时间(60、90、120、150、180 min)对总黄酮得率的影响。
1.2.2.2 不同料液比对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响
设定提取时间90 min,提取温度75 ℃,乙醇体积分数75%,考察料液比(1:20、1:30、1:40、1:50、1:60 g/mL)对总黄酮得率的影响。
1.2.2.3 不同提取温度对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响
设定提取时间90 min,料液比(1:40 g/mL),乙醇体积分数75%,考察提取温度(55、65、75、85、95 ℃)对总黄酮得率的影响。
1.2.2.4 不同乙醇体积分数对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响
设定提取时间90 min,料液比(1:40 g/mL),提取温度65 ℃,考察乙醇体积分数(55%、65%、75%、85%、95%)对总黄酮得率的影响。
1.2.3 响应面试验
在单因素实验基础上,以各显著影响因素为自变量。利用Design-Expert 8.0.6软件和Box-Behnken设计进行4因素3水平的响应面试验,实验选取提取时间(A)、料液比(B)、提取温度(C)、乙醇体积分数(D)为自变量,半枝莲总黄酮得率(Y)为响应值,优化半枝莲总黄酮的提取工艺,因素及水平设计见表1。
表 1 响应面试验设计因素与水平Table 1. Design factors and levels of response surface experiment水平 因素 A提取时间
(min)B料液比
(g/mL)C提取温度
(℃)D乙醇体积分数
(%)−1 60 1:30 55 65 0 90 1:40 65 75 1 120 1:50 75 85 1.2.4 半枝莲总黄酮的纯化
按照最优工艺制得半枝莲总黄酮提取溶液,减压浓缩至含生药浓度为0.2 g/mL的浓缩液,备用。参考前期预实验结果及半枝莲总黄酮纯化工艺的文献[25−26]报道,采用AB-8大孔吸附树脂纯化,湿法装柱(层析柱内径2.5 cm,高25 cm),树脂径高比1:6。上样浓度为浓缩液所稀释后的样品溶液,浓度为10 mg/mL,样品体积为3 BV,上样流速为2 mL/min,水洗量为3 BV以去除杂质,后用40%乙醇4 BV洗脱,洗脱体积流量为2 mL/min。减压浓缩后进行冷冻干燥,处理得半枝莲总黄酮纯化物。分别取适量半枝莲粗黄酮和经过纯化后的总黄酮冻干粉于25 mL容量瓶中,加75%的乙醇定容制成浓度为20 mg/mL的样品溶液,按照1.2.1.4方法下方法测得半枝莲总黄酮纯化后的得率。
1.2.5 体外抗氧化活性分析
1.2.5.1 DPPH自由基清除能力的测定
参考文献[27−28]方法并稍作修改,精密称取半枝莲总黄酮纯化物和维生素C适量,分别加乙醇制成浓度为2.5 mg/mL的储备液备用。精密吸取各储备液后加乙醇稀释得质量浓度为5、10、25、50、100、200、400、600 μg/mL的样品溶液。每个质量浓度设6个复孔,阳性组采用维生素C代替样品溶液。吸取100 μL样品溶液于96孔板中,等量加入DPPH溶液,混匀,避光反应30 min,517 nm波长下检测吸光度。根据吸光度计算样品对DPPH自由基的清除能力,实验重复三次,并利用Graphpad prism 9.5.0软件计算半枝莲总黄酮纯化物和维生素C对DPPH自由基清除率的IC50值。计算DPPH自由基清除率公式如下:
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=[1−A1−A2A0]×100 式中:A0为乙醇+DPPH溶液的吸光度;A1为样品溶液+DPPH溶液的吸光度;A2为样品溶液+乙醇的吸光度。
1.2.5.2 ABTS+自由基清除能力的测定
参考文献[29−30]并适当优化,将制备的ABTS储备液用50%乙醇溶液稀释。调节其吸光值在734 nm波长下为0.7±0.05,即得ABTS工作液。将半枝莲总黄酮纯化物用50%乙醇稀释成质量浓度为5、10、25、50、100、200、400、600 μg/mL的样品溶液,维生素C作为阳性对照组,每个质量浓度设置6个复孔。分别吸取10 μL供试品样液与200 μL ABTS工作液加入到96孔板中,避光孵育8 min,在734 nm下测定吸光值。根据吸光度计算样品对ABTS+自由基清除能力,实验重复三次,并利用Graphpad prism 9.5.0软件计算半枝莲总黄酮纯化物和维生素C对ABTS+自由基清除率的IC50值。计算ABTS+自由基清除率公式如下:
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=[1−A1−A2A0]×100 式中:A0为50%乙醇+ABTS 工作液的吸光度;A1为样品溶液+ABTS 工作液的吸光度;A2为样品溶液+50%乙醇的吸光度。
1.2.6 体外抗肿瘤活性的测定
1.2.6.1 细胞培养
将人非小细胞肺癌NCI-H1299细胞培养于含10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培养基中,人肝癌HepG2细胞、人高转移性肝癌MHCC-97H细胞、人肝癌HuH-7细胞分别培养在含10%胎牛血清的DMEM高糖培养基中,均于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中常规培养。
1.2.6.2 抗肿瘤活性测定
参考文献[31−32]方法,取处于对数生长期的NCI-H1299细胞、HepG2细胞、MHCC-97H细胞、HuH-7细胞,分别经0.25%胰蛋白酶消化、离心、制成悬液后调整细胞密度NCI-H1299细胞为8×104 个/mL,其余细胞密度为1×105 个/mL,接种于96孔细胞培养板中,每孔100 μL,于37 ℃、5% CO2条件下培养24 h至细胞完全贴壁,弃去原培养液。实验设置空白组、对照组和样品组。空白组中无细胞只含相应完全培养基,对照组中含细胞与相应培养基,样品组中依此加入总黄酮纯化物浓度为50、100、200、300、400、500、600 μg/mL的完全培养液。每组设置5个复孔,分别培养24 h。
培养结束后,每孔加入浓度为5 mg/mL的MTT溶液(10 μL每孔),在培养箱中孵育4 h后吸去上清,每孔加入DMSO溶液(150 μL每孔),避光处理,摇床上低速振荡10 min,酶标仪490 nm波长下测定吸光度,根据下式计算细胞存活率。
细胞存活率(%)=(A样品−A空白A对照−A空白)×100 1.3 数据处理
试验均设计三次平行实验,运用Excel 2019、Orign 2021、Design-Expert 13、Graphpad Prism 9.5.0等软件对数据进行处理及统计分析,其中MTT实验数据采用单因素方差分析,以P<0.05视作差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验
2.1.1 提取时间对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响
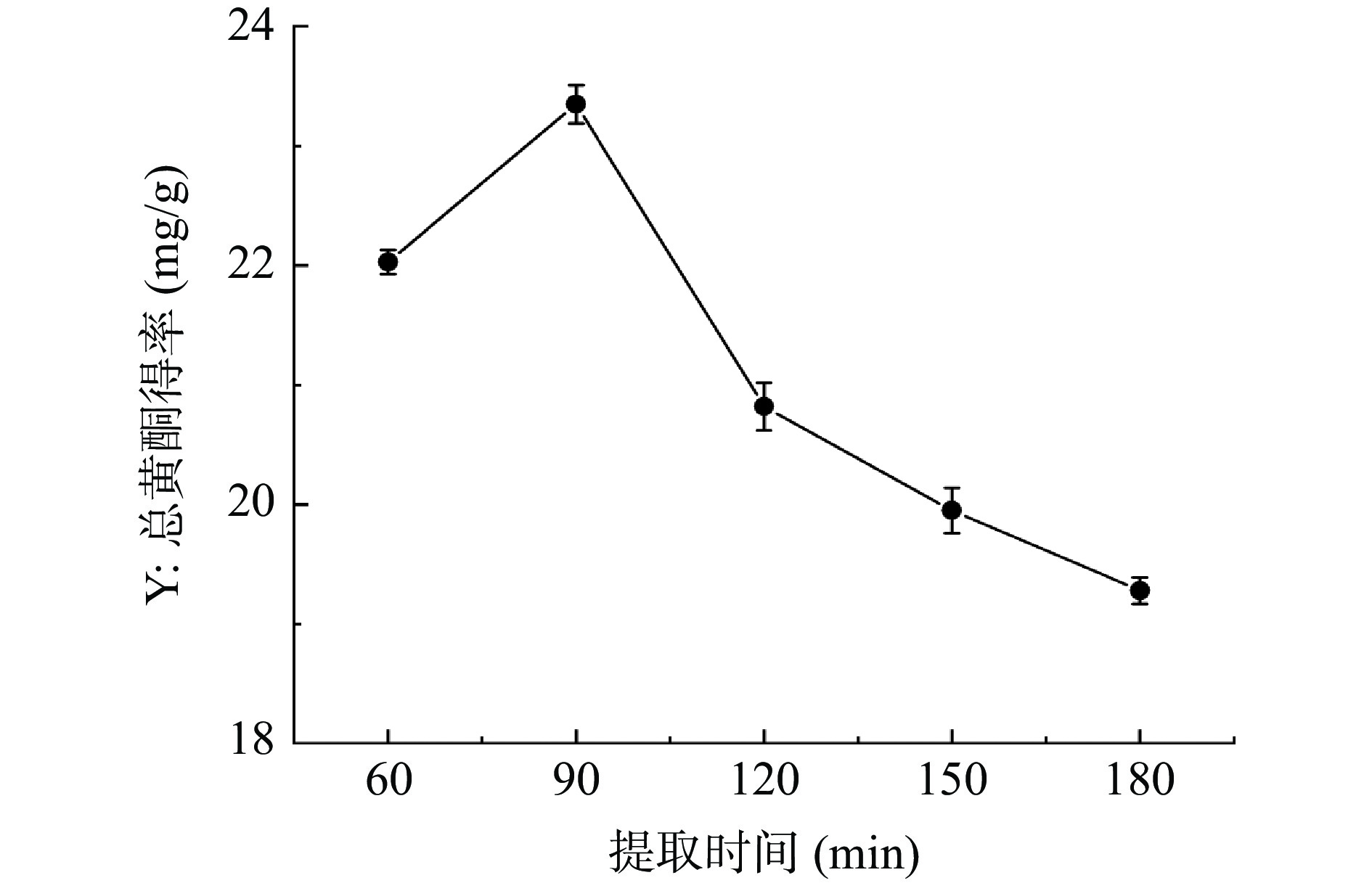
提取时间对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响如图1所示,提取时间在60~90 min时,半枝莲总黄酮得率随着时间的延长逐渐增加,在提取时间为90 min时,总黄酮得率达到最大值,得率由22.03±0.10 mg/g升高到23.35±0.16 mg/g。提取时间超过90 min后,总黄酮得率随着时间的増加反而出现下降趋势,这可能是因为回流时间越长,乙醇的挥发性越大从而导致乙醇浓度降低,促使黄酮的提取能力减弱,也可能是此时黄酮类化合物已经基本溶出[33],延长回流时间黄酮类成分也变化不大,甚至可能造成部分热敏性的黄酮成分发生降解[34],还会影响其他物质的溶出。因此,选择提取时间60~120 min进行响应面优化试验。
2.1.2 料液比对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响
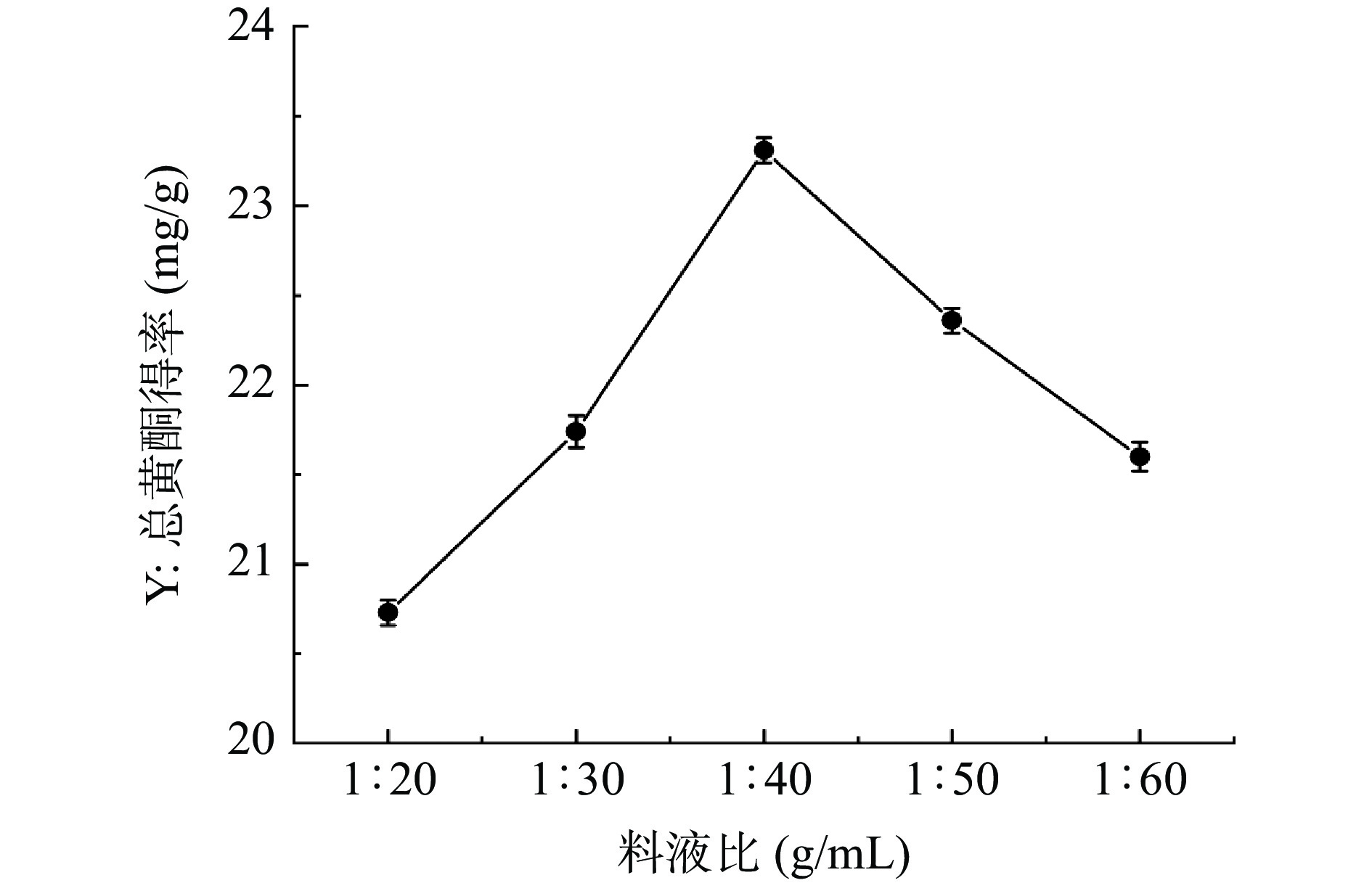
料液比对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响如图2所示,随着料液比的增加,半枝莲总黄酮得率呈现先升高后下降的趋势,总黄酮得率在料液比为1:40(g/mL)时达到最大值,得率为23.31±0.07 mg/g。当溶剂体积倍数超过40倍时,总黄酮得率明显降低,至21.60±0.08 mg/g。其原因可能是在一定范围内,随着料液比的增加会促进黄酮类物质的溶出,超过此范围可能会导致其他成分的溶出以及使某些黄酮类成分的结构被破坏,从而导致黄酮得率降低[35]。因此,选择料液比1:30~1:50 g/mL进行响应面优化试验。
2.1.3 提取温度对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响
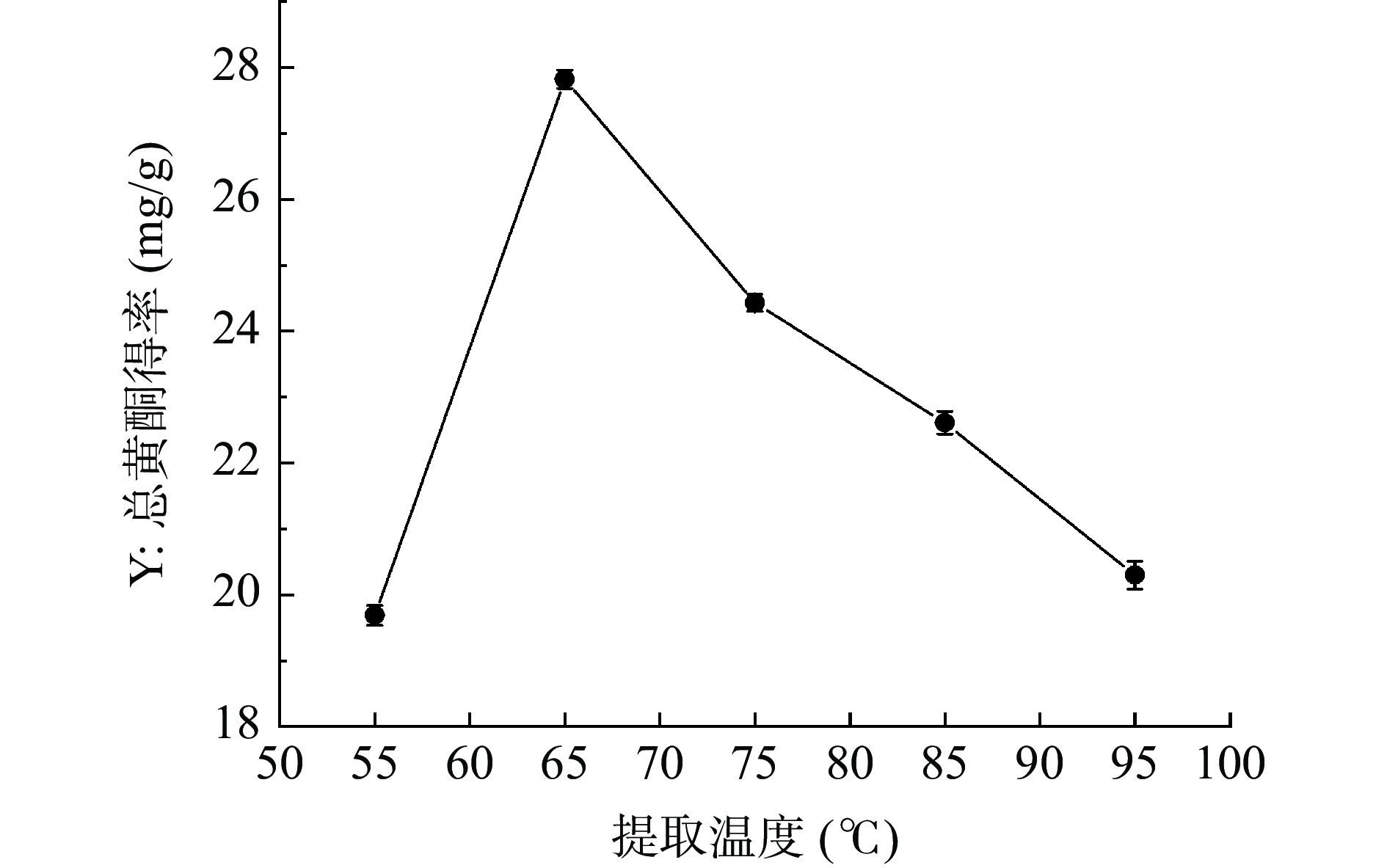
提取温度对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响如图3所示,当温度在55~65 ℃的时候总黄酮得率随着温度升高而升高,并在提取温度为65 ℃时达到最大值,为27.82±0.14 mg/g,当温度高于65 ℃时,半枝莲总黄酮得率明显下降,这可能是因为随着温度的适当增加,分子运动速度及溶解渗透能力增强,故提取效果好[36]。但温度太高,导致热敏性的黄酮类成分结构遭受破坏,部分黄酮成分氧化,从而黄酮得率降低。因此选择提取温度为55~75 ℃进行响应面优化试验。
2.1.4 乙醇体积分数对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响
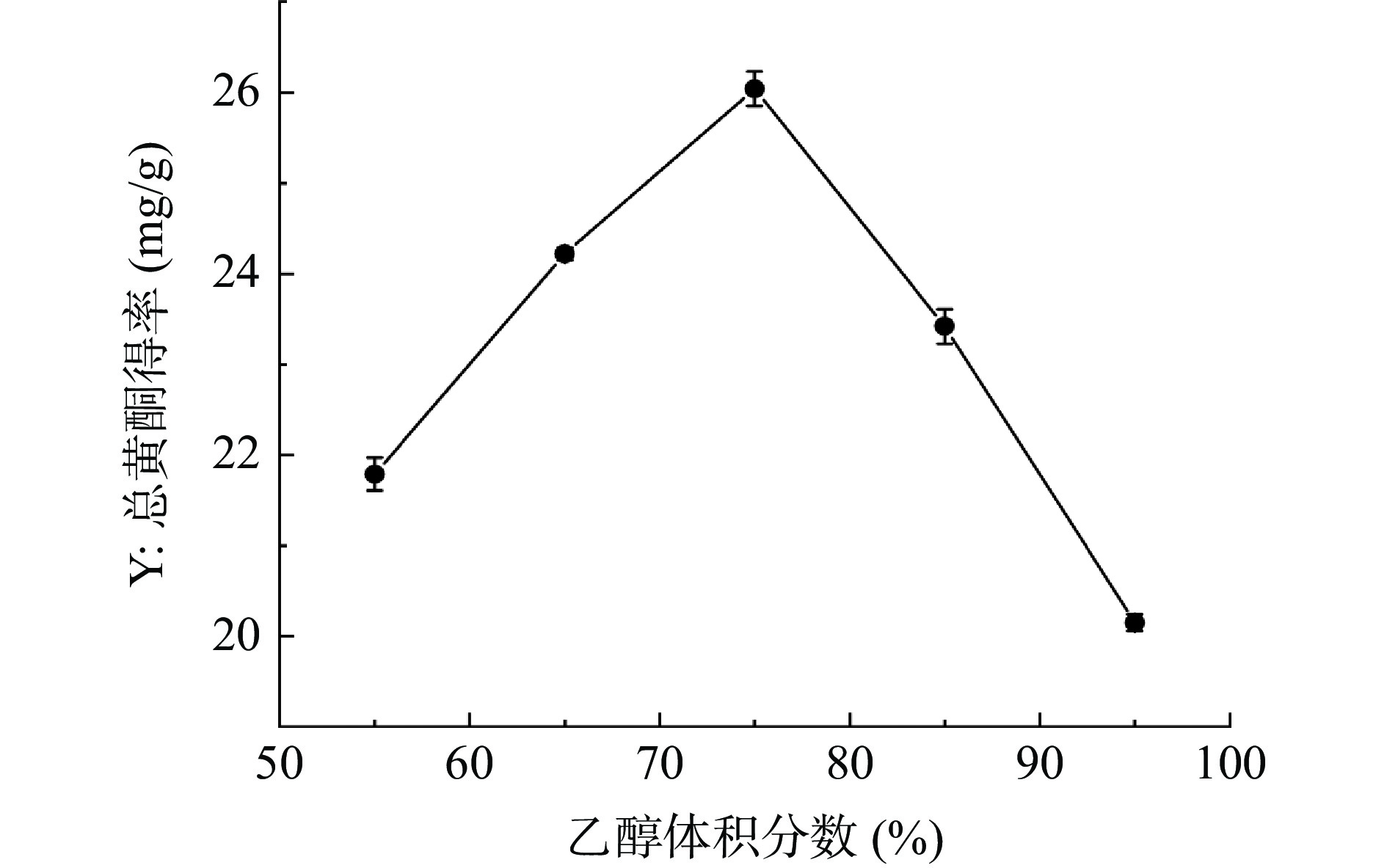
乙醇体积分数对半枝莲总黄酮得率的影响如图4所示,当乙醇体积分数为55%~75%时,半枝莲总黄酮得率明显增加,且在乙醇体积分数为75%时达到最大值,为26.04±0.19 mg/g,当乙醇体积分数大于75%时,黄酮得率减小,这可能是因为当乙醇浓度超过一定范围时,会使醇溶性的色素及极性更小的脂溶性成分溶出变多,这些溶剂会与黄酮类化合物竞争溶剂,从而导致黄酮类成分的溶出能力降低[37]。因此选择乙醇体积分数为65%~85%进行响应面优化试验。
2.2 响应面试验结果
2.2.1 响应试验设计结果
利用软件Design-Expert 8.0.6进行试验设计并对试验数据进行回归拟合,得半枝莲总黄酮得率(Y)对提取时间(A)、料液比(B)、提取温度(C)、乙醇体积分数(D)的二元回归模拟方程:Y=2.57+0.0664A+0.0685B+0.1291C−0.0866D−0.0722AB+0.0034AC+0.0468AD+0.0592BC+0.0209BD+0.1049CD−0.2524A2−0.2928B2−0.1830C2−0.3434D2。响应试验结果见表2。
表 2 响应面试验结果及分析Table 2. Results and analysis of response surface experiment实验号 因素 总黄酮得率Y(mg/g) A B C D 1 −1 −1 0 0 18.74 2 0 0 0 0 27.03 3 0 −1 0 1 18.64 4 0 1 1 0 24.29 5 0 0 0 0 25.13 6 0 0 −1 1 17.39 7 0 0 0 0 26.05 8 0 1 0 −1 19.88 9 −1 0 1 0 21.65 10 −1 0 0 1 17.47 11 1 0 −1 0 21.23 12 0 0 −1 −1 21.68 13 0 0 0 0 25.69 14 0 0 1 −1 21.98 15 −1 0 −1 0 19.55 16 0 −1 1 0 19.98 17 −1 1 0 0 21.10 18 1 0 0 −1 20.29 19 0 1 0 1 19.13 20 0 −1 0 −1 20.22 21 1 0 1 0 23.47 22 1 0 0 1 19.39 23 0 −1 −1 0 17.99 24 0 0 0 0 24.66 25 1 1 0 0 20.90 26 −1 0 0 −1 20.24 27 1 −1 0 0 21.43 28 0 1 −1 0 19.93 29 0 0 1 1 21.88 2.2.2 响应面回归模型方差分析
响应回归模型方差见表3,由表3可知:该模型的F=15.25,P<0.0001,表明所得模型极显著,失拟项为P值为0.5390>0.05,不显著,表明实验结果主要受所选因素影响受其他因素影响很小,方程式成立,方法可靠。模型的复合相关系数R2=0.9385,说明该模型拟合程度良好,可以用该模型优化半枝莲中总黄酮的提取工艺。根据F值可知所考察的因素对响应值影响力的大小顺序为提取温度(C)>乙醇体积分数(D)>料液比(B)>提取时间(A),其中一次项中提取温度与乙醇体积分数交互作用对结果影响显著,其他交互作用影响不显著,二次项中四个因素对结果均有极显著影响。
表 3 回归方程方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of regression equations来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 模型项 178.71 14 12.77 15.22 <0.0001 A 5.28 1 5.28 6.30 0.0250 B 5.64 1 5.64 6.73 0.0212 C 19.97 1 19.97 23.81 0.0002 D 9.00 1 9.00 10.73 0.0055 AB 2.09 1 2.09 2.49 0.1369 AC 0.0049 1 0.0049 0.0058 0.9402 AD 0.8742 1 0.8742 1.04 0.3246 BC 1.40 1 1.40 1.67 0.2166 BD 0.1722 1 0.1722 0.2054 0.6574 CD 4.39 1 4.39 5.23 0.0382 A2 41.37 1 41.37 49.33 <0.0001 B2 55.66 1 55.66 66.37 <0.0001 C2 21.74 1 21.74 25.92 0.0002 D2 76.51 1 76.51 91.22 <0.0001 残差 11.74 14 0.8387 失拟项 8.44 10 0.8444 1.02 0.5375 纯误差 3.30 4 0.8243 总差 190.45 28 R2=0.9383 R2adj=0.8767 2.2.3 响应面试验交互作用分析
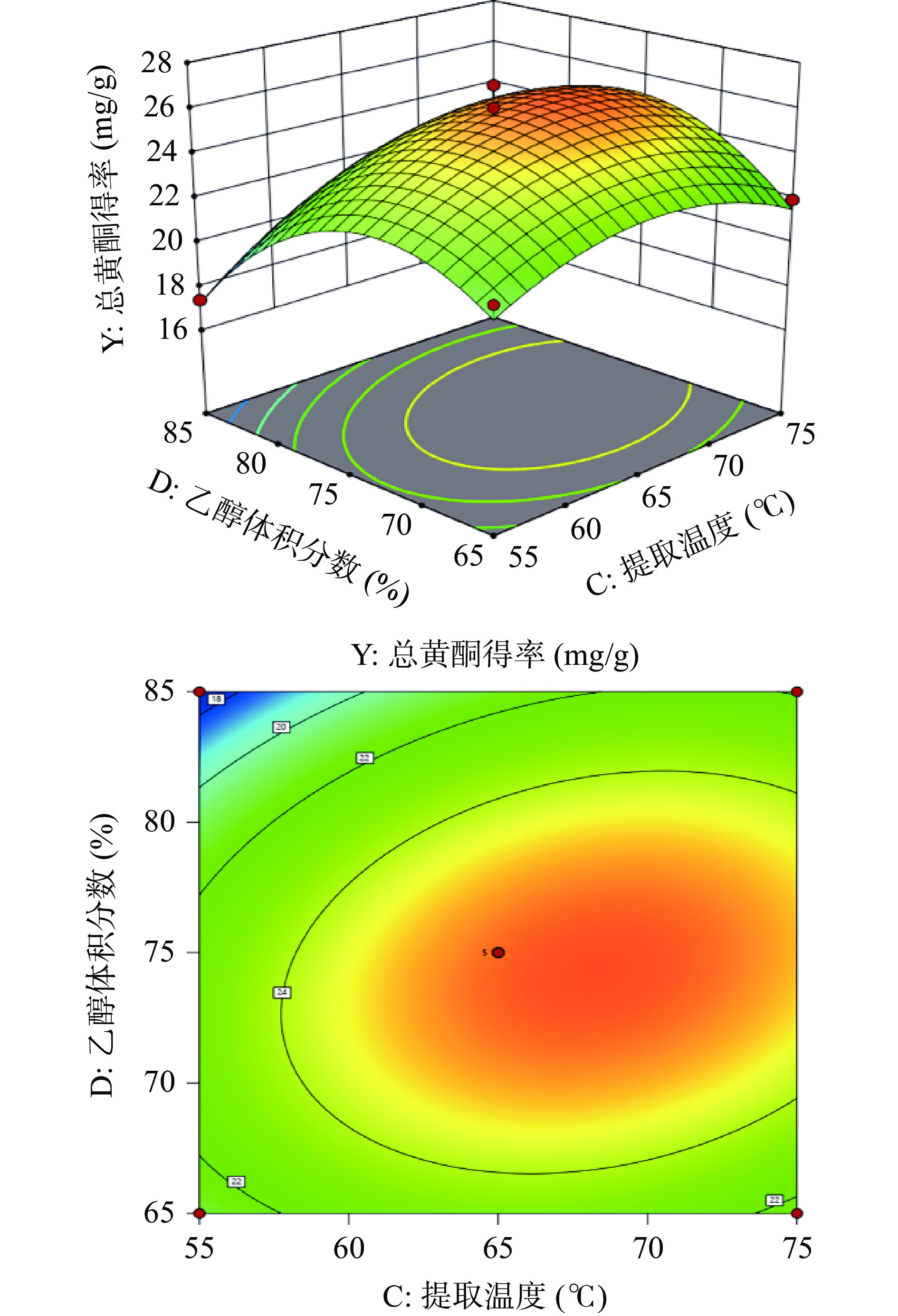
根据回归方程,绘制出提取温度(C)和乙醇体积分数(D)交互项的响应面和等高线图,如图5所示。响应面越陡峭且倾斜程度越大则说明该图中两因素间的交互作用越显著;等高线呈现椭圆形且线之间越密集则说明交互作用越明显[38]。从图5中可看出提取温度与乙醇体积分数的响应面图呈陡峭状且等高线图呈椭圆形,说明提取温度与乙醇体积分数之间的交互作用显著,直观分析结果与方差分析结果一致。
2.2.4 最佳提取工艺的确定与验证
响应面模型优化的最优提取工艺为提取时间93.2443 min,料液比1:41.3804(g/mL),提取温度68.5852 ℃,乙醇体积分数74.4041%,预测此条件下总黄酮得率为26.05 mg/g。为便于工业生产及实际操作的可行性,确定最终工艺为提取时间93 min,料液比1:41(g/mL),提取温度68 ℃,乙醇体积分数75%。采用该提取方法进行3次平行实验,总黄酮得率的均值为26.46 mg/g,与预测值的相对误差为1.56%,表明经优化的提取工艺可行且稳定,可用于半枝莲总黄酮的提取。
半枝莲总黄酮经大孔树脂纯化后的得率为60.13 mg/g,纯度为49.32%,比粗提取(17.35%)纯度增大2.84倍左右。
2.3 半枝莲总黄酮抗氧化活性测定
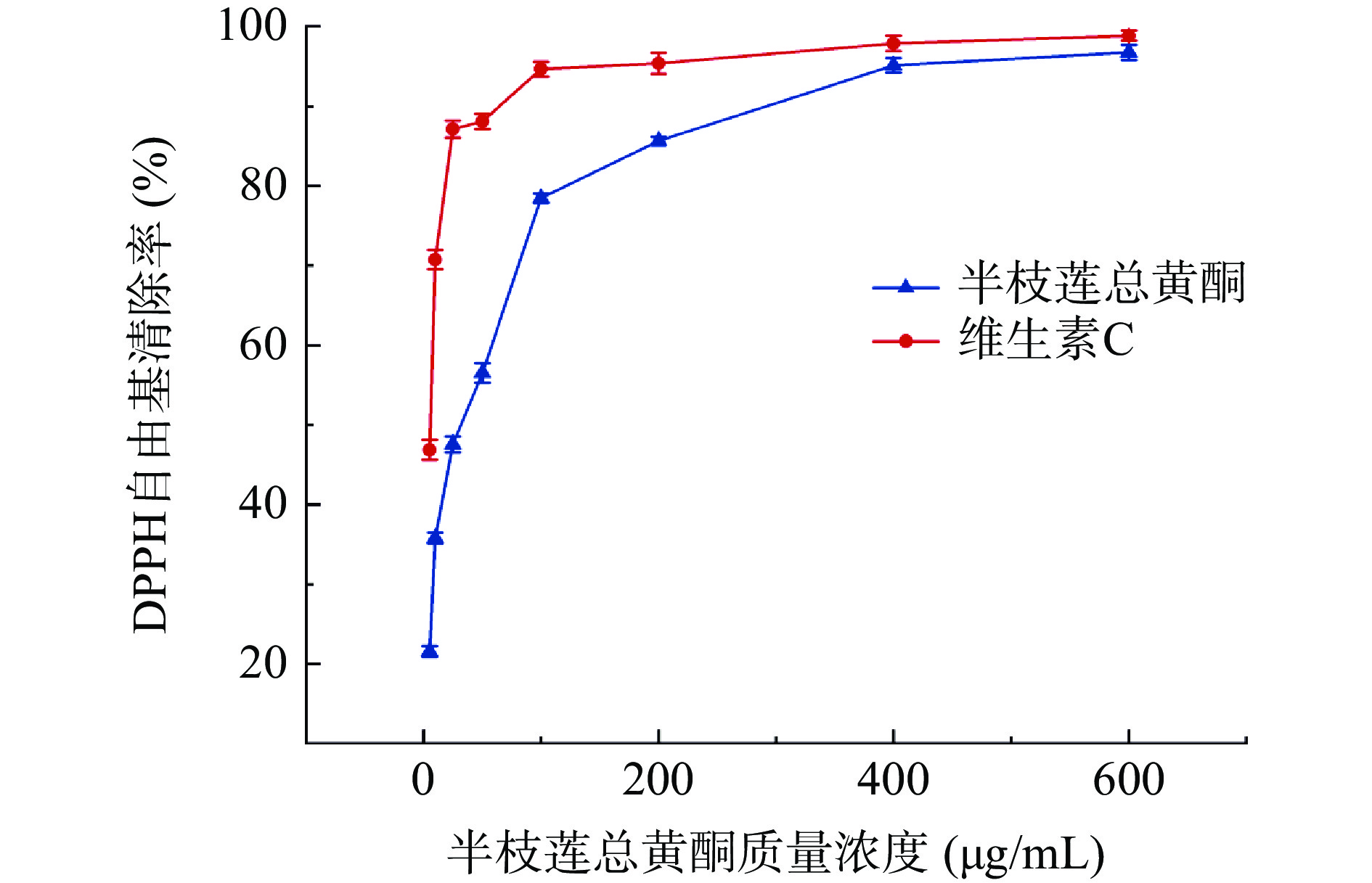
2.3.1 半枝莲总黄酮纯化物对DPPH自由基的清除作用
半枝莲总黄酮纯化物对DPPH自由基的清除作用如图6所示,当半枝莲总黄酮纯化物质量浓度在5~600 μg/mL的范围内,对DPPH自由基的清除能力随着质量浓度的增加而增大,呈现量效关系。当质量浓度在400 μg/mL时对DPPH自由基的清除能力开始接近阳性药物维生素C,当质量浓度为600 μg/mL时,自由基清除率达到96.75%,几乎与阳性药维生素C的自由基清除率(98.86%)相当。此外根据文献[39−40]调查发现,近年来对半枝莲黄酮的抗氧化能力大多是评价粗提物的自由基清除能力,对纯化后的总黄酮未见研究。因此在此次实验中发现在相同浓度时,经纯化后的半枝莲总黄酮比粗提物的自由基清除能力更强。则进一步说明该提取方式可行且纯化后的总黄酮比粗提取的自由基清除能力更强,因此,对半枝莲粗提取进行纯化试验可减少药物资源的浪费,同时增强该成分的抗氧化活性。利用Graphpad prism软件计算半枝莲总黄酮纯化物和维生素C对DPPH自由基清除率的IC50分别为25.41、5.07 μg/mL。可见,与维生素C相比,半枝莲总黄酮纯化物对DPPH自由基清除率略弱。
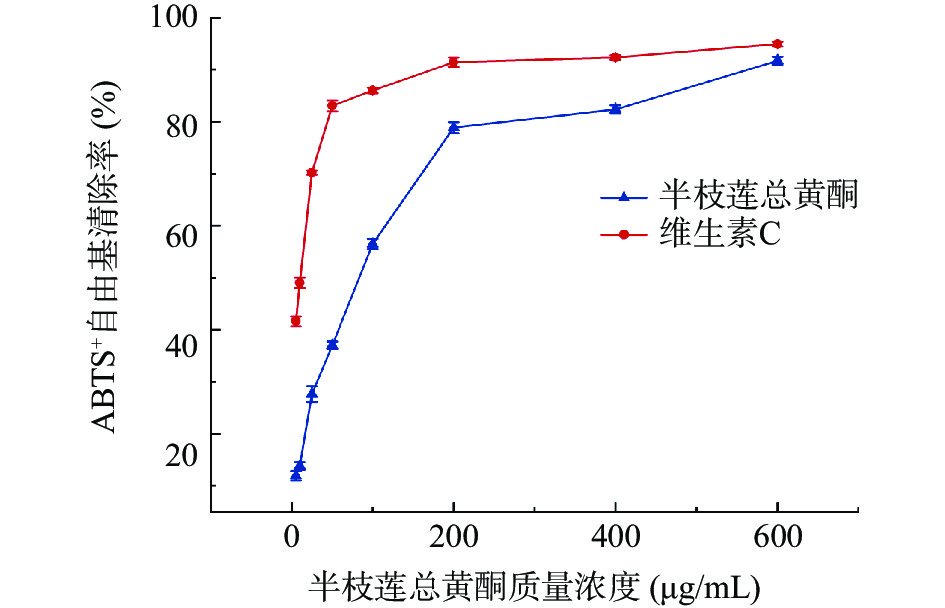
2.3.2 半枝莲总黄酮纯化物对ABTS+自由基的清除作用
半枝莲总黄酮纯化物对ABTS+自由基的清除作用如图7所示,ABTS+自由基的清除能力随半枝莲总黄酮纯化物的浓度升高而加强,且呈现量效关系。当质量浓度为600 μg/mL时,清除率达到91.75%,此时ABTS+自由基的清除能力接近于维生素C的自由基清除率(94.96%)。同时根据Graphpad prism软件分析,得出半枝莲总黄酮纯化物IC50=70.41 μg/mL和维生素C的IC50=8.56 μg/mL,这说明,在相同浓度下,半枝莲总黄酮纯化物对ABTS+的自由基清除率比维生素C相对较弱。
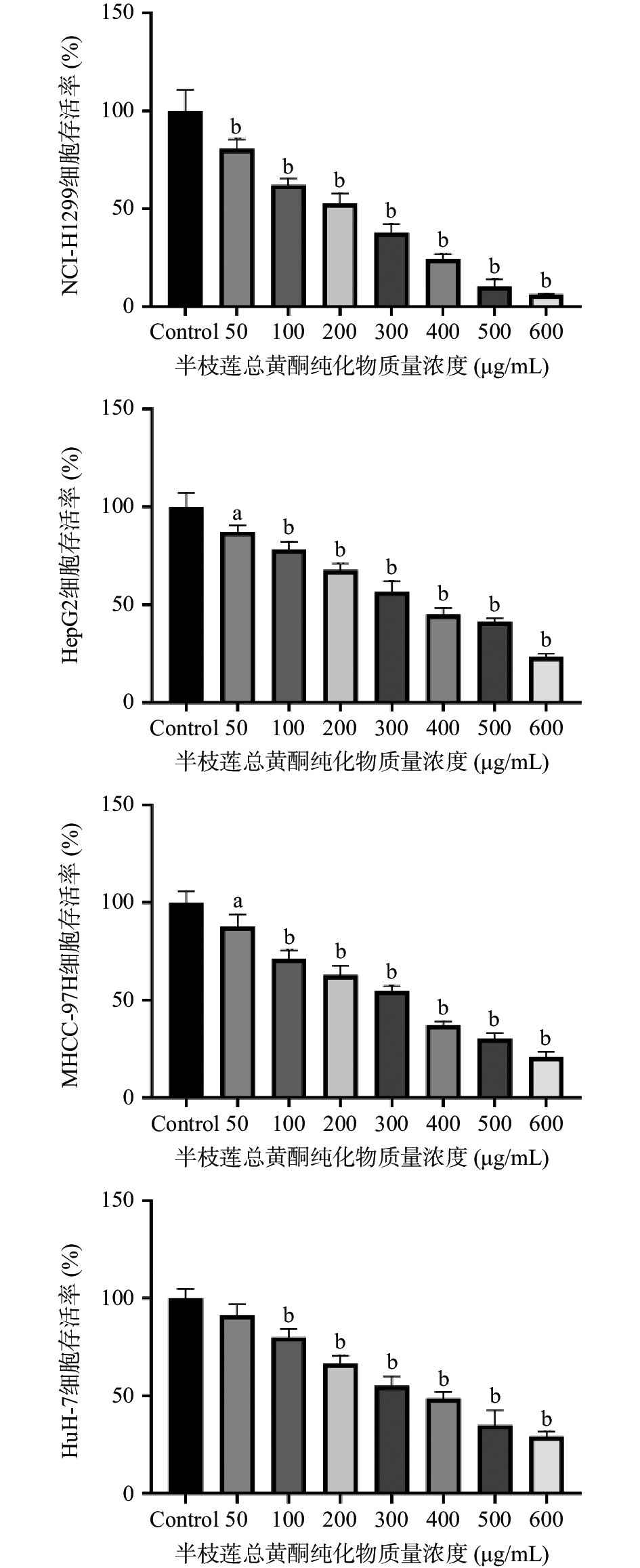
2.4 半枝莲总黄酮纯化物抗肿瘤活性测定结果
半枝莲总黄酮纯化物对肺癌NCI-H1299细胞、肝癌HepG2细胞、MHCC-97H细胞、HuH-7细胞活性试验结果如图8所示,由图可知,对于人肝癌HuH-7细胞,除质量浓度为50 μg/mL组外,其余各药物浓度组对肝癌细胞的存活率与对照组相比较均有显著抑制作用(P<0.0001)。此外,半枝莲总黄酮纯化物对以下4种肿瘤细胞均能产生不同程度的抑制作用,当半枝莲总黄酮的质量浓度增加时,细胞存活率出现显著降低趋势,且呈现剂量-效应关系,其中以NCI-H1299细胞更明显,IC50分别为168.6、330.5、269.2、335.8 μg/mL。
3. 结论
本研究采用溶剂提取法,经单因素实验结合响应曲面试验,最终确定半枝莲总黄酮最优提取条件为提取时间93 min,料液比1:41(g/mL),提取温度68 ℃,乙醇体积分数75%,总黄酮得率为26.46 mg/g。所获得的半枝莲总黄酮提取工艺稳定、可靠,能够为半枝莲总黄酮的新药研发、产品开发等提供理论依据。
本实验利用AB-8型大孔吸附树脂对最佳提取工艺提取后的总黄酮进行富集纯化,并对纯化后得到的总黄酮进行体外抗氧化及抗肿瘤活性评价。其中抗氧化实验结果表明纯化后的半枝莲总黄酮与同样采用溶剂提取法的半枝莲总黄酮粗提物相比在同一浓度上有更强的抗氧化能力,且纯化后的总黄酮抗氧化能力与该质量浓度呈现明显的量效关系,清除DPPH自由基的能力较清除ABTS+自由基强,但其机理尚不明确,仍需进一步探究。相较维生素C对照组,在较高浓度时表现出与阳性组相当的抗氧化活性,能够为半枝莲总黄酮在食品、药品等产品研发、新型抗氧剂研发等领域提供新的研究方向。抗肿瘤实验中,采用MTT法检测细胞活性,结果表明纯化后的总黄酮提取物对4种肿瘤细胞均有一定抑制作用,其中对NCI-H1299细胞的抑制作用更明显,其增殖抑制能力依次为肺癌NCI-H1299细胞>MHCC-97H细胞>HepG2细胞>HuH-7细胞,这提示半枝莲总黄酮在治疗肺癌和肝癌方面有较好的应用前景,可为开发以半枝莲尤其是半枝莲总黄酮为原料的,具有广泛临床应用价值和商业开发价值的抗肿瘤新药提供理论和实验依据。
-
表 1 响应面试验设计因素与水平
Table 1 Design factors and levels of response surface experiment
水平 因素 A提取时间
(min)B料液比
(g/mL)C提取温度
(℃)D乙醇体积分数
(%)−1 60 1:30 55 65 0 90 1:40 65 75 1 120 1:50 75 85 表 2 响应面试验结果及分析
Table 2 Results and analysis of response surface experiment
实验号 因素 总黄酮得率Y(mg/g) A B C D 1 −1 −1 0 0 18.74 2 0 0 0 0 27.03 3 0 −1 0 1 18.64 4 0 1 1 0 24.29 5 0 0 0 0 25.13 6 0 0 −1 1 17.39 7 0 0 0 0 26.05 8 0 1 0 −1 19.88 9 −1 0 1 0 21.65 10 −1 0 0 1 17.47 11 1 0 −1 0 21.23 12 0 0 −1 −1 21.68 13 0 0 0 0 25.69 14 0 0 1 −1 21.98 15 −1 0 −1 0 19.55 16 0 −1 1 0 19.98 17 −1 1 0 0 21.10 18 1 0 0 −1 20.29 19 0 1 0 1 19.13 20 0 −1 0 −1 20.22 21 1 0 1 0 23.47 22 1 0 0 1 19.39 23 0 −1 −1 0 17.99 24 0 0 0 0 24.66 25 1 1 0 0 20.90 26 −1 0 0 −1 20.24 27 1 −1 0 0 21.43 28 0 1 −1 0 19.93 29 0 0 1 1 21.88 表 3 回归方程方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of regression equations
来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 模型项 178.71 14 12.77 15.22 <0.0001 A 5.28 1 5.28 6.30 0.0250 B 5.64 1 5.64 6.73 0.0212 C 19.97 1 19.97 23.81 0.0002 D 9.00 1 9.00 10.73 0.0055 AB 2.09 1 2.09 2.49 0.1369 AC 0.0049 1 0.0049 0.0058 0.9402 AD 0.8742 1 0.8742 1.04 0.3246 BC 1.40 1 1.40 1.67 0.2166 BD 0.1722 1 0.1722 0.2054 0.6574 CD 4.39 1 4.39 5.23 0.0382 A2 41.37 1 41.37 49.33 <0.0001 B2 55.66 1 55.66 66.37 <0.0001 C2 21.74 1 21.74 25.92 0.0002 D2 76.51 1 76.51 91.22 <0.0001 残差 11.74 14 0.8387 失拟项 8.44 10 0.8444 1.02 0.5375 纯误差 3.30 4 0.8243 总差 190.45 28 R2=0.9383 R2adj=0.8767 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中国药典[M]. 一部. 北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2020:122. [National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese pharmacopoeia[M]. Part1. Beijing:China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020:122. National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese pharmacopoeia[M]. Part1. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 122.
[2] 王刚, 孙丹丹, 张云丽, 等. 半枝莲抗肿瘤作用研究进展[J]. 食品与药品,2022,24(4):377−381. [WANG G, SUN D D, ZHANG Y L, et al. Research progress on anti-tumor effects of Scutellariae Barbatae Herba[J]. Food and Drug,2022,24(4):377−381. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-979X.2022.04.020 WANG G, SUN D D, ZHANG Y L, et al . Research progress on anti-tumor effects of Scutellariae Barbatae Herba[J]. Food and Drug,2022 ,24 (4 ):377 −381 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-979X.2022.04.020[3] 李娜, 王平, 孙铁锋, 等. 半枝莲化学成分、药理作用及质量控制研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志,2020,45(21):5117−5128. [LI N, WANG P, SUN T F, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological action and quality control of Scutellaria barbata[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2020,45(21):5117−5128. LI N, WANG P, SUN T F, et al . Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological action and quality control of Scutellaria barbata[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2020 ,45 (21 ):5117 −5128 .[4] 杜义龙, 李艳荣, 洪霞, 等. 基于指纹图谱和多组分定量分析的半枝莲质量评价研究[J]. 中草药, 54(2):670−676. [DU Y L, LI Y R, HONG X, et al. Quality evaluation of Scutellaria barbata based on combination of chromatographic fingerprints and multi-component quantitative analysis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 54(2):670−676. DU Y L, LI Y R, HONG X, et al. Quality evaluation of Scutellaria barbata based on combination of chromatographic fingerprints and multi-component quantitative analysis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 54(2): 670−676.
[5] 蒋家璐, 康安, 李琴, 等. UHPLC-QTRAP-MS结合化学计量学分析半枝莲中多指标成分[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,47(2):437−443. [JIANG J L, KANGA, LI Q, et al. Multi-index components of Scutellariae barbatae Herba according to UHPLC-QTRAP-MS coupled with chemometrics[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2022,47(2):437−443. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210901.201 JIANG J L, KANGA, LI Q, et al . Multi-index components of Scutellariae barbatae Herba according to UHPLC-QTRAP-MS coupled with chemometrics[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2022 ,47 (2 ):437 −443 . doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210901.201[6] 许晶, 石凤芹, 杜可心, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨“半枝莲-白花蛇舌草”抗乳腺癌的作用机制[J]. 中国中药杂志,2020,45(18):4448−4454. [XU J, SHI F Q, DU K X, et al. Mechanism of " Scutellaria barbata-Hedyotis diffusa" against breast cancer based on network pharmacology[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2020,45(18):4448−4454. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200302.502 XU J, SHI F Q, DU K X, et al . Mechanism of "Scutellaria barbata-Hedyotis diffusa" against breast cancer based on network pharmacology[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2020 ,45 (18 ):4448 −4454 . doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200302.502[7] KULBAT W K, ORACZ J, ŻYŻELEWICZ D. Bioactive properties of extracts from Plectranthus barbatus (Coleus forskohlii) roots received using various extraction methods[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(24):8986.
[8] CHEN Q, RAHMAN K, WANG S J, et al. Scutellaria barbata:A review on chemical constituents, pharmacological activities and clinical applications[J]. Current Pharmaceutical Design,2020,26(1):160−175. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666191216124310
[9] MENEZES J C, CAMPOS V R. Natural biflavonoids as potential therapeutic agents against microbial diseases[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,769:145168. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145168
[10] GUO S, ZHANG L, WU S, et al. Research progress of typical flavonoids in improving insulin resistance[J]. Archives of Medical Science-Atherosclerotic Diseases,2020,5(1):335−342. doi: 10.5114/amsad.2020.103472
[11] LIN H, WANG X, LI Z, et al. Total flavonoids of Rhizoma drynariae promote angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone defects[J]. Phytotherapy Research,2022,36(9):3584−3600. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7525
[12] IVANOVIĆ S, AVRAMOVIĆ N, DOJČINOVIĆ B, et al. Chemical composition, total phenols and flavonoids contents and antioxidant activity as nutritive potential of roasted hazelnut skins ( Corylus avellana L.)[J]. Foods,2020,9(4):430. doi: 10.3390/foods9040430
[13] BERCZYŃSKI P, KŁADNA A, KRUK I, et al. Synthesis and in vitro antioxidant activity study of some new piperazinyl flavone compounds[J]. Luminescence,2017,32(8):1431−1441. doi: 10.1002/bio.3342
[14] 陈俊其, 秦华珍, 尹优, 等. 山姜属中药黄酮类成分提取及分离富集方法研究进展[J]. 中医学报,2019,34(11):2302−2307. [CHEN J Q, QIN H Z, YIN Y, et al. Research progress on extraction, separation and enrichment methods of flavonoids from Chinese medicine of alpinia[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine,2019,34(11):2302−2307. doi: 10.16368/j.issn.1674-8999.2019.11.533 CHEN J Q, QIN H Z, YIN Y, et al . Research progress on extraction, separation and enrichment methods of flavonoids from Chinese medicine of alpinia[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine,2019 ,34 (11 ):2302 −2307 . doi: 10.16368/j.issn.1674-8999.2019.11.533[15] ZHANG L, JIANG Y, PANG X, et al. Simultaneous optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction for flavonoids and antioxidant activity of Angelica-keiskei using response surface methodology (RSM)[J]. Molecules,2019,24(19):3461. doi: 10.3390/molecules24193461
[16] RUAN C, XIAO X, LI G. Microwave‐assisted extraction coupled with countercurrent chromatography for the rapid preparation of flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata D. Don[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2014,37(11):1364−1369. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201400168
[17] 王京龙, 于定荣, 张超, 等. 3种提取方法对二黄汤中5种成分在大鼠体内药动学的影响[J]. 中成药,2021,43(1):1−5. [WANG J L, YU D R, ZHANG C, et al. Effects of three extraction methods on the pharmacokinetics offive constituents in Erhuang decoction in rats in vivo[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2021,43(1):1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.01.001 WANG J L, YU D R, ZHANG C, et al . Effects of three extraction methods on the pharmacokinetics offive constituents in Erhuang decoction in rats in vivo[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2021 ,43 (1 ):1 −5 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.01.001[18] 钟烜钰, 王弘, 杨金易, 等. 植物基原料游离多酚的提取与分离纯化方法研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(20):6620−6627. [ZHONG X Y, WANG H, YANG J Y, et al. Research progress of extraction, separation and purification method of free polyphenols in plant-based raw materials[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(20):6620−6627. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2022.20.021 ZHONG X Y, WANG H, YANG J Y, et al . Research progress of extraction, separation and purification method of free polyphenols in plant-based raw materials[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022 ,13 (20 ):6620 −6627 . doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2022.20.021[19] KIM M K, PARK G, JI Y, et al. Design of experiments-based optimization of flavonoids extraction from daphne genkwa flower buds and flavonoids contents at different blooming stages[J]. Plants,2022,11(7):925. doi: 10.3390/plants11070925
[20] 金顺琪, 张露蓉, 李曼, 等. 鲜半枝莲高效液相色谱指纹图谱的建立及10种黄酮类成分含量测定[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2022,42(2):119−122. [JIN S Q, ZHANG L R, LI M, et al. Establishment of HPLC fingerprints of Fresh Scutellaria barbata and determination of 10 flavonoids components[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy,2022,42(2):119−122. doi: 10.13286/j.1001-5213.2022.02.03 JIN S Q, ZHANG L R, LI M, et al . Establishment of HPLC fingerprints of Fresh Scutellaria barbata and determination of 10 flavonoids components[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy,2022 ,42 (2 ):119 −122 . doi: 10.13286/j.1001-5213.2022.02.03[21] 陈瑞鑫, 蒋运斌, 陈文莉, 等. 不同产地独一味总黄酮的质量评价[J]. 中国药房,2023,34(4):419−422,428. [CHEN R X, JAING Y B, CHEN W L, et al. Quality evaluation of total flavonoids of Lamiophlomis rotata from different producing areas[J]. China Pharmacy,2023,34(4):419−422,428. CHEN R X, JAING Y B, CHEN W L, et al . Quality evaluation of total flavonoids of Lamiophlomis rotata from different producing areas[J]. China Pharmacy,2023 ,34 (4 ):419 −422,428 .[22] 张磊, 梁雅丽, 郭钧. 半枝莲茎中黄酮类化合物提取及抗氧化分析[J]. 食品工程,2022(1):30−34. [ZHANG L, LAING Y L, GUO J. Extraction and antioxidant analysis of flavonoids from the stems of Scutellaria barbata[J]. Food Engineering,2022(1):30−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6044.2022.01.009 ZHANG L, LAING Y L, GUO J . Extraction and antioxidant analysis of flavonoids from the stems of Scutellaria barbata[J]. Food Engineering,2022 (1 ):30 −34 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6044.2022.01.009[23] 何根祥, 谭梅英, 詹利之. 中心复合设计法在半枝莲总黄酮提取工艺中的应用[J]. 湖南中医杂志, 2017, 33(1):152−153,187. [HE G X, TAN M Y, ZHAN L Z. Application of central composite design in extraction processfortotal flavonoids in Scutellaria barbata[J]. Hunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 33(1):152−153,187. HE G X, TAN M Y, ZHAN L Z. Application of central composite design in extraction processfortotal flavonoids in Scutellaria barbata[J]. Hunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 33(1): 152−153,187.
[24] 戴丛书, 柴晶美, 林长青. 金银花黄酮提取物的降血糖作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(24):386−393. [DAI C S, CHAI J M, LIN C Q. Hypoglycemic effect of flavonoid extract from Lonicera japonica thunb[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(24):386−393. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022030191 DAI C S, CHAI J M, LIN C Q . Hypoglycemic effect of flavonoid extract from Lonicera japonica thunb[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (24 ):386 −393 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022030191[25] 白天雅, 高子怡, 赵二劳. 半枝莲中黄酮提取纯化研究进展[J]. 吉林农业,2018(21):68−69. [BAI T Y, GAO Z Y, ZHAO E L. Progress in the extraction and purification of flavonoids from Scutellaria barbat[J]. Agriculture of Jilin,2018(21):68−69. doi: 10.14025/j.cnki.jlny.2018.21.031 BAI T Y, GAO Z Y, ZHAO E L . Progress in the extraction and purification of flavonoids from Scutellaria barbat[J]. Agriculture of Jilin,2018 (21 ):68 −69 . doi: 10.14025/j.cnki.jlny.2018.21.031[26] 刘丹, 郭珊珊, 吕子明, 等. 半枝莲总黄酮AB-8型大孔吸附树脂纯化工艺优选[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(22):19−23. [LIU D, GUO S S, LÜ Z M, et al. Optimization of purification technology for total flavonoids from Scutellariae barbatae herba by AB-8 macroporous resin[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2013,19(22):19−23. LIU D, GUO S S, LÜ Z M, et al . Optimization of purification technology for total flavonoids from Scutellariae barbatae herba by AB-8 macroporous resin[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2013 ,19 (22 ):19 −23 .[27] ZHANG L, REN B, ZHANG J, et al. Anti-tumor effect of Scutellaria barbata D. Don extracts on ovarian cancer and its phytochemicals characterisation[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2017,206:184−192. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.05.032
[28] 邴鑫, 尚红梅, 娄玉杰. 响应面优化串叶松香草总黄酮的提取工艺及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(4):137−142,149. [BING X, SHANG H M, LOU Y J. Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from cup plant by response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(4):137−142,149. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.04.026 BING X, SHANG H M, LOU Y J . Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from cup plant by response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018 ,39 (4 ):137 −142,149 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.04.026[29] GONG J, HUANG J, XIAO G, et al. Antioxidant capacities of fractions of bamboo shaving extract and their antioxidant components[J]. Molecules,2016,21(8):996. doi: 10.3390/molecules21080996
[30] 雷秋琪, 叶诗洁, 黄永康, 等. 菱角壳黄酮提取工艺优化及抑肿瘤细胞增殖活性作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(14):224−232. [LEI Q Q, YE S J, HUANG Y K, et al. Optimization of extraction process of flavonoids from water chestnut shell and effect on anti-tumor cell proliferation activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(14):224−232. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021100178 LEI Q Q, YE S J, HUANG Y K, et al . Optimization of extraction process of flavonoids from water chestnut shell and effect on anti-tumor cell proliferation activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (14 ):224 −232 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021100178[31] JIANG Y, LI D, MA X, et al. Ionic liquid–ultrasound-based extraction of biflavonoids from Selaginella helvetica and investigation of their antioxidant activity[J]. Molecules,2018,23(12):3284. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123284
[32] LI D, QIAN Y, TIAN Y J, et al. Optimization of ionic liquid-assisted extraction of biflavonoids from Selaginella doederleinii and evaluation of its antioxidant and antitumor activity[J]. Molecules,2017,22(4):586. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040586
[33] 孙悦, 刘晓冰, 苏卓文, 等. 微波辅助低共熔溶剂提取鹰嘴豆中黄酮及其抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(14):120−128. [SUN Y, LIU X B, SUW Z, et al. Extraction of flavonoids from chickpeas by microwave-assisted eutectic solvent and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(14):120−128. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.14.020 SUN Y, LIU X B, SUW Z, et al . Extraction of flavonoids from chickpeas by microwave-assisted eutectic solvent and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020 ,41 (14 ):120 −128 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.14.020[34] 宋代荣, 刘昌衡, 贾爱荣, 等. 罗汉参皮总黄酮的提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业,2022,43(8):69−74. [SONG D R, LIU C H, JIA A R, et al. Optimization of the extraction process of total flavonoids from the peel of Apios americana medic and study on its antioxidant activity[J]. The Food Industry,2022,43(8):69−74. SONG D R, LIU C H, JIA A R, et al . Optimization of the extraction process of total flavonoids from the peel of Apios americana medic and study on its antioxidant activity[J]. The Food Industry,2022 ,43 (8 ):69 −74 .[35] CHEBROLU K K, JAYAPRAKASHA G K, JIFON J, et al. Optimization of flavanones extraction by modulating differential solvent densities and centrifuge temperatures[J]. Talanta,2011,85(1):353−362. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2011.03.075
[36] ZHANG L, YU J, XU Q, et al. Evaluation of total phenolic, flavonoid, carbohydrate contents and antioxidant activities of various solvent extracts from Angelica amurensis root[J]. Natural Product Research,2021,35(21):4084−4088. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2020.1716349
[37] 张家音, 李浩楠, 雷嗣超, 等. 板栗壳黄酮提取工艺优化及其组成分析[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(6):50−59. [ZHANG J Y, LI H N, LEI S C, et al. Optimization of extraction process and composition analysis of flavonoids from chestnut shell[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(6):50−59. ZHANG J Y, LI H N, LEI S C, et al . Optimization of extraction process and composition analysis of flavonoids from chestnut shell[J]. Food Research and Development,2022 ,43 (6 ):50 −59 .[38] WU E Y, SUN W J, WANG Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of total flavonoids from Abrus cantoniensis (Abriherba) by response surface methodology and evaluation of its anti-inflammatory effect[J]. Molecules,2022,27(7):2036. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072036
[39] 陈红梅, 谢翎. 响应面法优化半枝莲黄酮提取工艺及体外抗氧化性分析[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(2):45−50. [CHEN H M, XIE L. Optimization of extraction process for flavonoid from Soutellaria barbata by response surface methodology and evaluation of its antioxidant activity[J]. Food Science,2016,37(2):45−50. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201602008 CHEN H M, XIE L . Optimization of extraction process for flavonoid from Soutellaria barbata by response surface methodology and evaluation of its antioxidant activity[J]. Food Science,2016 ,37 (2 ):45 −50 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201602008[40] 王润坤, 石绍奎, 宋玲祥. 响应面法优化半枝莲总黄酮微波提取工艺及其体外活性研究[J]. 中国药业,2020,29(15):37−41. [WANG R K, SHI S K, SONG L X. Optimization of microwave extraction technology of total flavonoids by response surface methodology and in vitro activity evaluation from Scutellaria barbata[J]. China Pharmaceuticals,2020,29(15):37−41. WANG R K, SHI S K, SONG L X . Optimization of microwave extraction technology of total flavonoids by response surface methodology and in vitro activity evaluation from Scutellaria barbata[J]. China Pharmaceuticals,2020 ,29 (15 ):37 −41 .





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
